Postman API Automation Testing in 2025: AI-Powered Assertion Hacks & EchoAPI vs Postman Guide
Use AI-driven, no-code assertions in Postman & EchoAPI to automate API testing in minutes—cut scripting effort by 90 % and catch every defect before CI/CD.
Why Do We Need API Assertions?
Let’s imagine we are testing the login API of an e-commerce platform. When we call the login endpoint, we receive the following response:
{
"status": "success",
"code": 1000,
"data": {
"user_id": "U12345",
"token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...",
"expire_time": "2025-06-01T12:00:00Z"
},
"message": "Login successful"
}
At this point, we need to verify:
- Whether the API returns a 200 status code (indicating the HTTP request was successful).
- Whether the business code is 1000 (indicating success).
- Whether the response time is under 500ms (to ensure performance).
- Whether the response body includes required fields like
user_idandtoken(to ensure correctness). - Whether the
Content-Typeisapplication/json(to ensure proper data format).
These checks are implemented through assertions. Assertions are a critical part of automated testing — they let us quickly determine whether an API behaves as expected, without manually inspecting each line of the response.
Postman Assertions in Action: Script-Driven Verification
In Postman, assertions are written in the [Scripts] → [Post-response] section using JavaScript.

Common Assertion Types and Their Implementations
1. Verify HTTP Status Code
pm.test("Should return 200 status code (HTTP request successful)", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
2. Verify Business Code
pm.test("Business code should be 1000 (success)", () => {
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(jsonData.errstr).to.eql(1000);
});
3. Verify Response Time
pm.test("Response time should be under 500ms (performance check)", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.responseTime).to.be.below(500);
});
4. Verify Response Body Structure
pm.test("Response body should contain user_id and token (correctness)", () => {
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(responseJson.data).to.have.all.keys("user_id", "token");
});
5. Verify Response Headers
pm.test("Content-Type should be JSON", () => {
pm.response.to.have.header("Content-Type", "application/json");
});
Running Tests and Viewing Results
After execution, assertion results can be viewed in the “Test Results” panel at the bottom of Postman.

EchoAPI Assertion Upgrade: AI + Visualization
Unlike Postman, where writing assertions requires coding skills, EchoAPI lowers the barrier with two major innovations.
AI-Generated Assertions: Zero-Code Quick Validation
Using the same login API example, you simply click the “AI Generate Assertions” button next to the response. EchoAPI will automatically analyze the response structure and generate assertions that cover status codes, response fields, and data types.
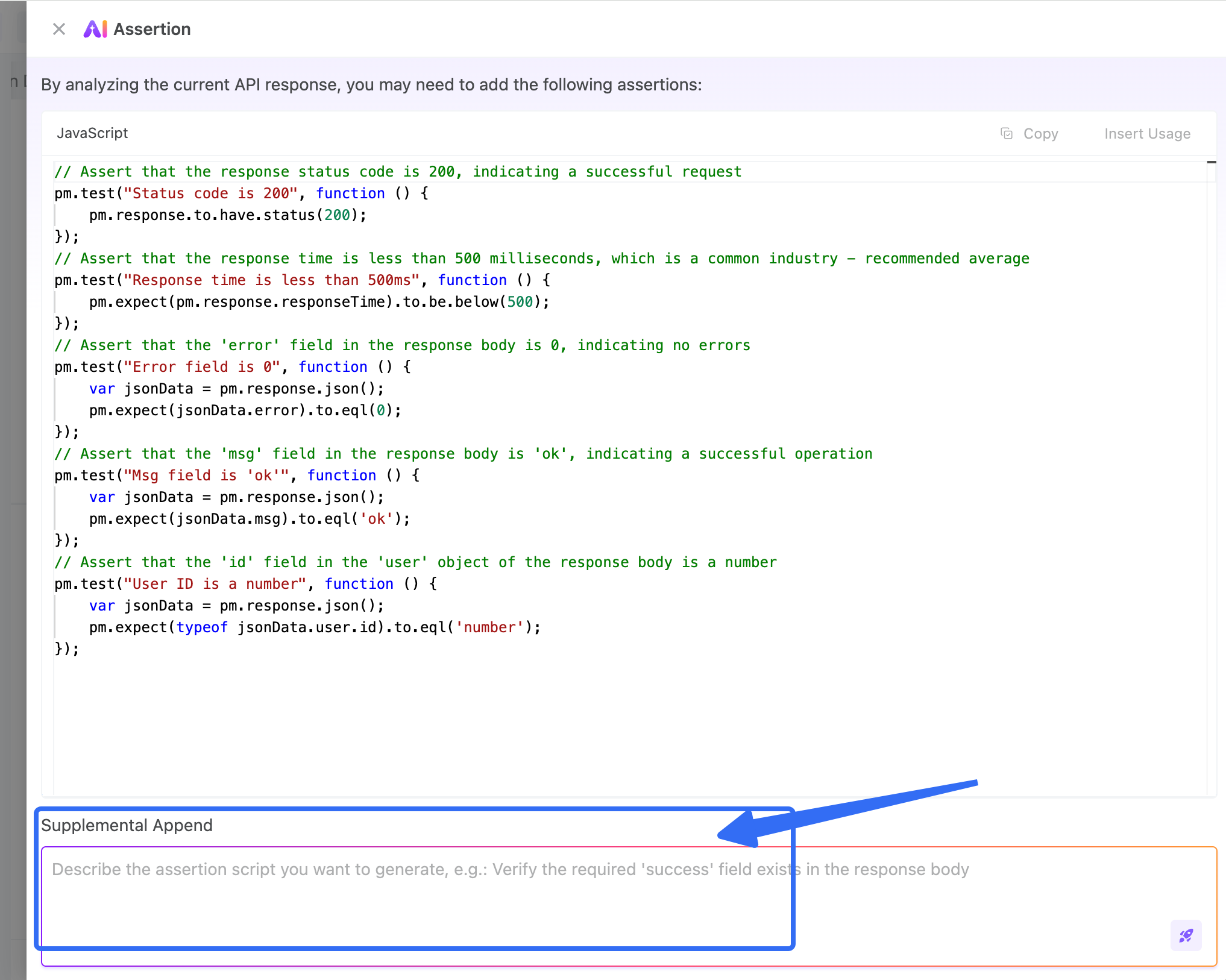
Supports iterative refinement: If the generated assertions are incomplete, you can add instructions such as “Add a check for non-empty token”.
Visual Assertion Builder: Zero-Code Interactive Setup
EchoAPI also provides a graphical interface to configure assertions in three simple steps:
- Go to Post-Processing → Add Assertion.
- Select the assertion type (Status Code / Response Time / Body / Header).
- Pick fields and conditions visually — no code required.
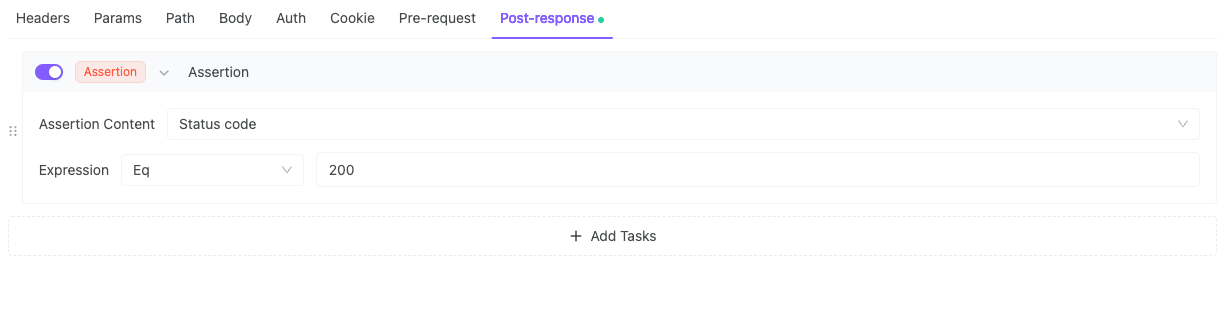
1. Verify HTTP Status Code = 200
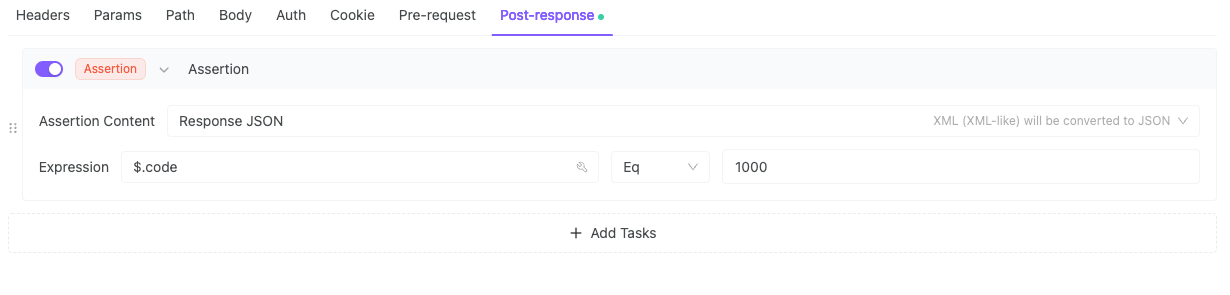
2. Verify Business Code = 1000
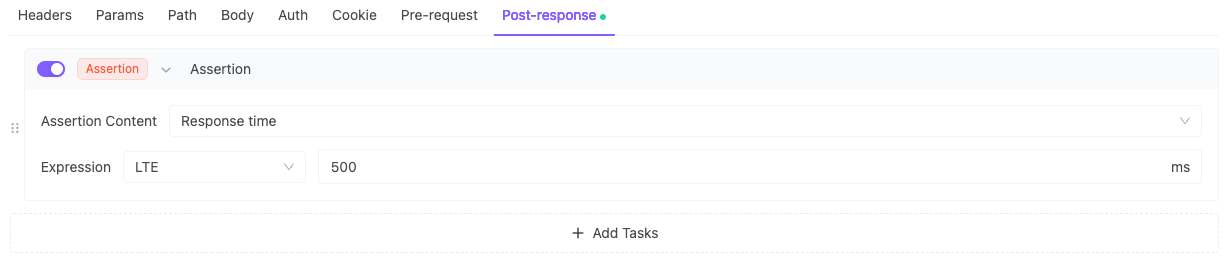
3. Verify Response Time < 500ms
4. Verify Response Body Contains user_id and token
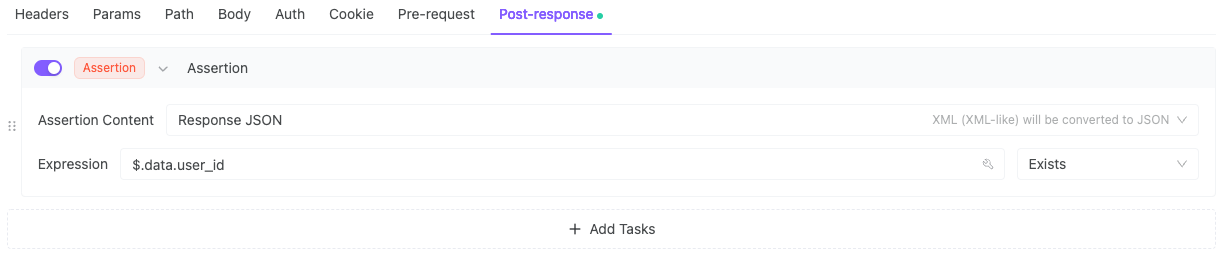
5. Verify Content-Type = application/json
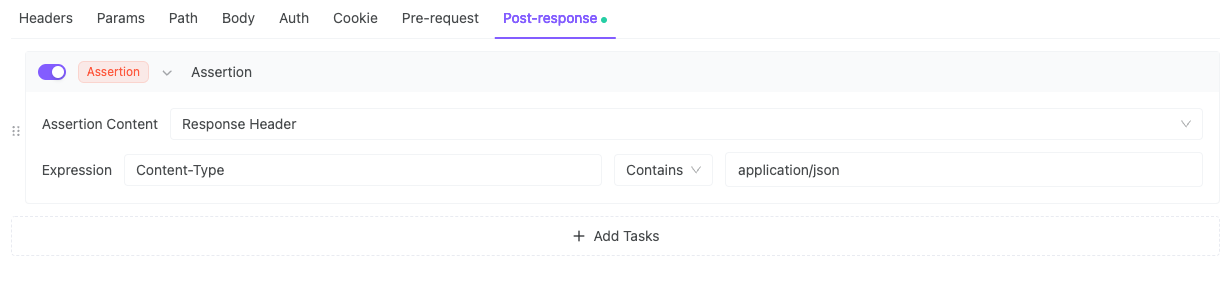
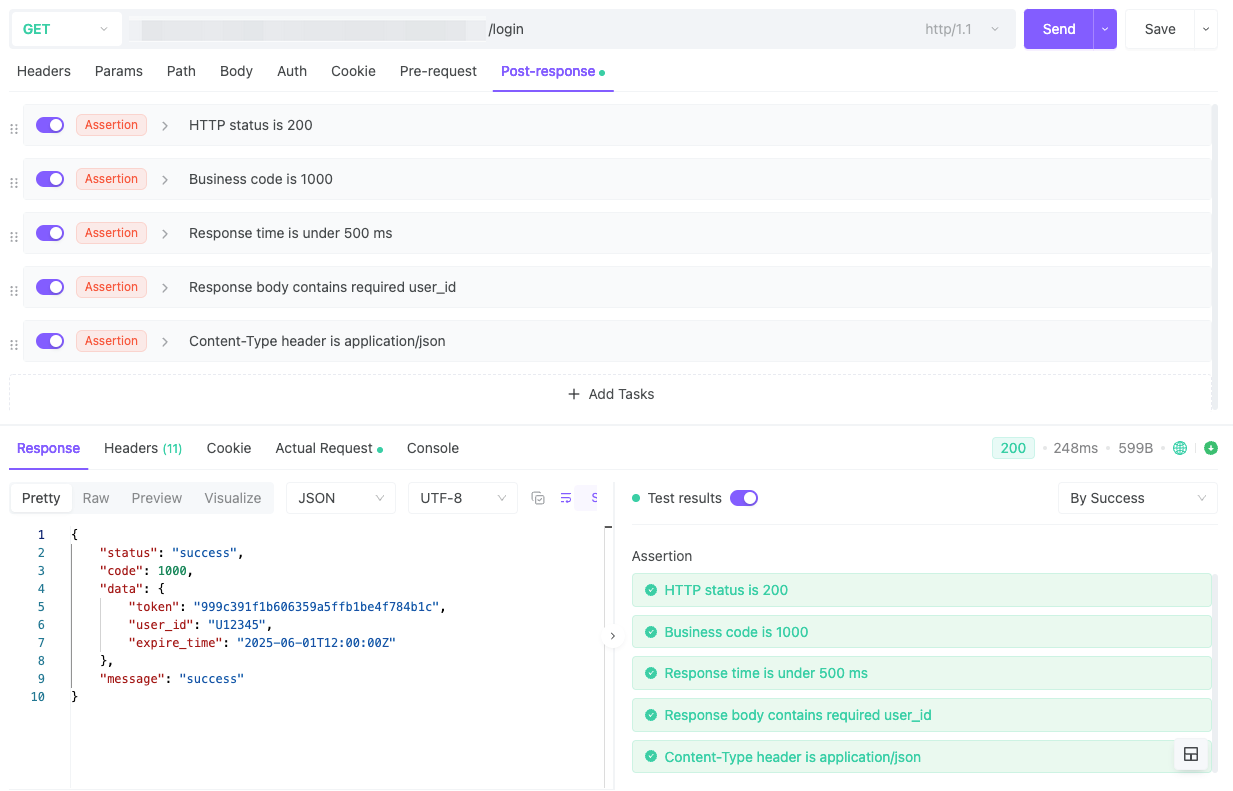
EchoAPI Assertion Execution and Results
When tests are executed, EchoAPI displays assertion results in a visual results panel:
- Green checkmarks ✅ = Passed assertions.
- Red crosses ❌ = Failed assertions with detailed error info.
Postman vs. EchoAPI: Which Assertion Tool Should You Use?
| Dimension | Postman | EchoAPI |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Requirement | Requires JavaScript knowledge | 1. 100% compatible with Postman scripts 2. Zero-code AI generation + Visual builder |
| Efficiency | Manual scripting, repetitive work | Auto-analyzes response, one-click assertions |
| Collaboration | Script-based management | Shared assertion rules + version control |
| Extensibility | Supports custom scripts | Custom scripts + AI generation + Visual assertions |
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Assertion Approach
- For technical teams: Postman remains a strong choice for complex, custom logic.
- For beginners or efficiency-focused teams: EchoAPI’s AI + Visual assertion features significantly improve productivity.
- Best practice: They’re not mutually exclusive. EchoAPI is fully compatible with Postman scripts, and any EchoAPI-generated assertions can be imported into Postman — ensuring a smooth toolchain.
Practical Recommendation: Use EchoAPI’s AI-powered assertions early in your API testing to quickly establish a baseline, then expand with visual assertions or Postman-compatible scripts for advanced cases. This creates a complete, scalable API automation workflow.




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server








