Mocking in API Development: Pain Points, Solutions, and Best Practices with EchoAPI
EchoAPI revolutionizes API mocking with dynamic, AI-powered simulations that accelerate development and eliminate backend dependencies, enabling seamless frontend progress and robust testing.
In everyday API development, mocking is almost unavoidable. Whether it’s fast iteration at the early stage of a project or when an endpoint isn’t ready yet, mocking ensures front-end development continues smoothly—even without real backend data.
1. Real-World Pain Points
Imagine this scenario:
You’re building a front-end for an e-commerce site. When a user clicks "Pay Now," your front-end calls the backend /pay endpoint, which should return something like:
{
"data": {
"code": 0,
"message": "success",
"pay_dtime":"2025-08-10 10:00:00",
"order_id":"sn12345678"
}
}
But the problems are:
- The backend isn’t ready, so you can’t test the post-payment flow.
- The payment API depends on an external gateway, not configured in the test environment.
- Some endpoints require complex authentication or data prep, making them unusable early.
Waiting on backend development blocks front-end progress—this is where mocking becomes critical.
2. Common Mocking Approaches & Limitations
2.1 Local JSON Files Mocking
Simplest approach: create mock/data.json and fetch it:
fetch('/mock/pay.json')
Drawbacks:
- Data is static; cannot simulate multiple scenarios.
- Cannot handle complex logic like pagination or conditional queries.
2.2 Front-End Request Interception (axios-mock-adapter, Mock.js)
Intercept requests in the browser:
mock.onPost('/api/pay/confirm').reply(200, {
"data": {
"code": 0,
"message": "success",
"pay_dtime":"2025-08-10 10:00:00",
"order_id":"sn12345678"
}
});
Drawbacks:
- Limited to use within the frontend project, making reuse difficult.
- Data embedded in code creates high maintenance and cleanup costs later.
2.3 Self-Hosted Mock Server (json-server, Easy Mock)
Run a separate mock services that return data when frontend requests are made.
Drawbacks:
- High setup and maintenance cost.
- Complex logic requires extra scripting; flexibility is limited.
These methods work for basic needs but lack flexibility and dynamic data generation as project complexity grows.
3. EchoAPI's Mock Capabilities and Practical Scenarios
EchoAPI offers a flexible and modern solution, supporting both rapid development and complex scenarios. Let's use the payment interface /pay as an example, simulating several return scenarios.
3.1 First Mock Capability of EchoAPI:Simulating Fixed Value Returns
Simulate a fixed response:
{
"data": {
"code": 0,
"message": "success"
}
}
In EchoAPI, create a new API with POST method and URL /pay. Then, in the "Design" - "Predefined Response Expectations" section, define it visually:
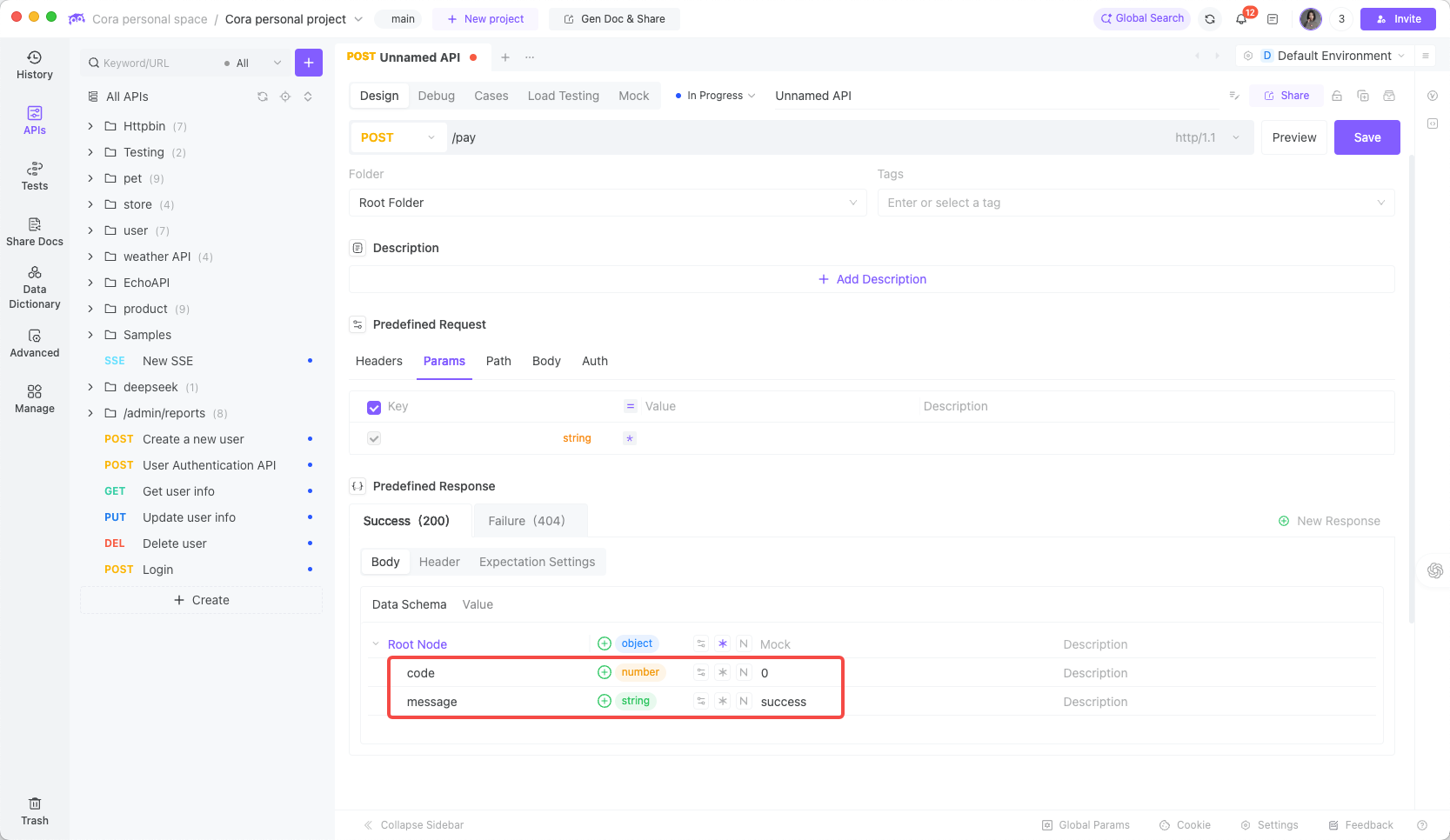
Then switch to the Mock tab to get the generated Mock URL:
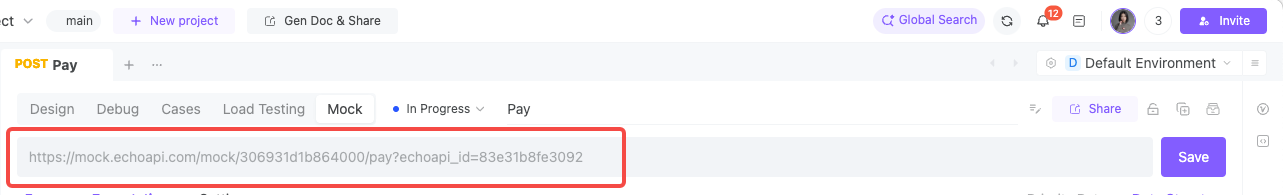
Calling this URL returns the predefined response:
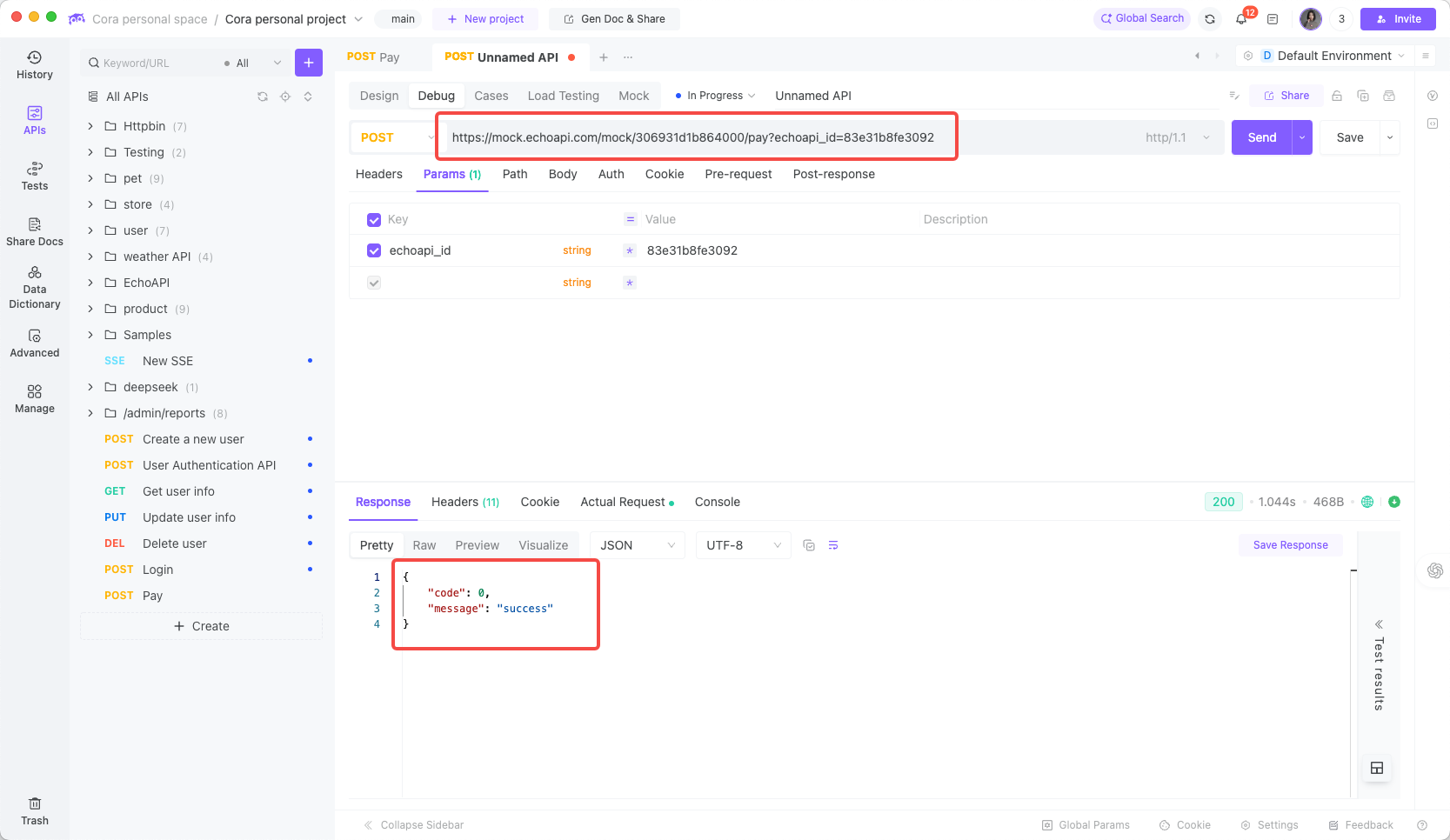
3.2 Second Mock Capability of EchoAPI: Generating Random Values Using Built-in Functions
When you need to add fields with real-time randomly generated values, like the pay_dtime date field in our example, EchoAPI provides abundant built-in variables for quickly generating various data types:
{
"data": {
"code": 0,
"message": "success",
"pay_dtime":"2025-08-10 10:00:00"
}
}
Simply add a new field, select "Mock Data" as the value source, and insert the appropriate built-in date variable:
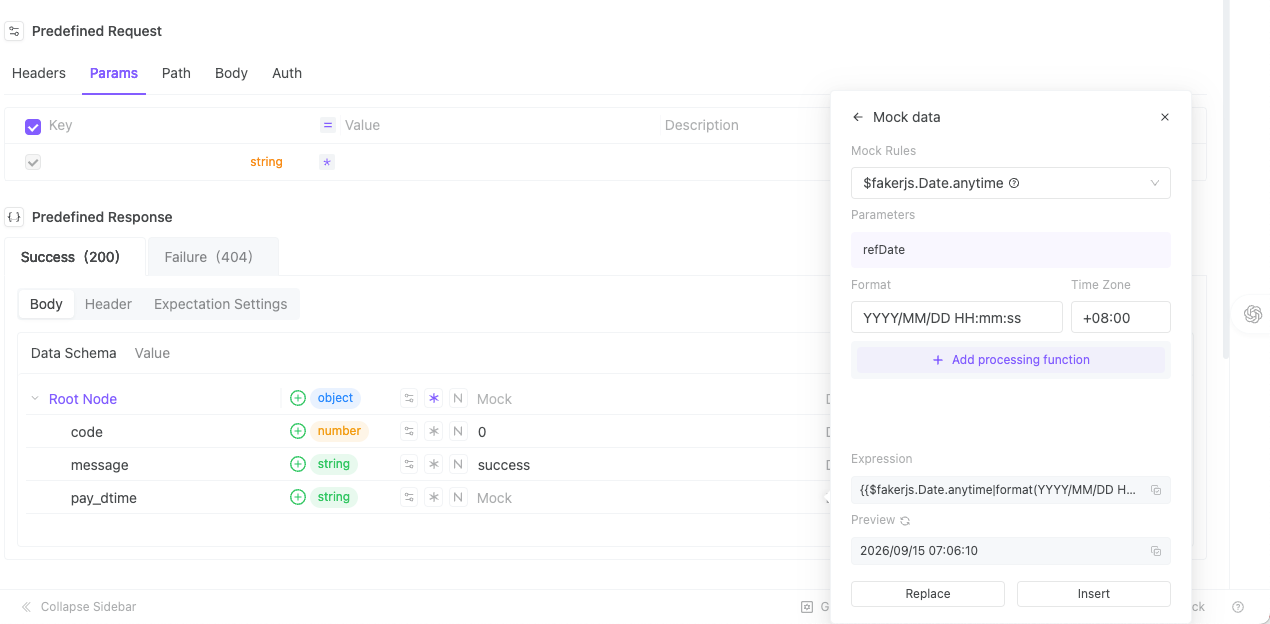
Example response:
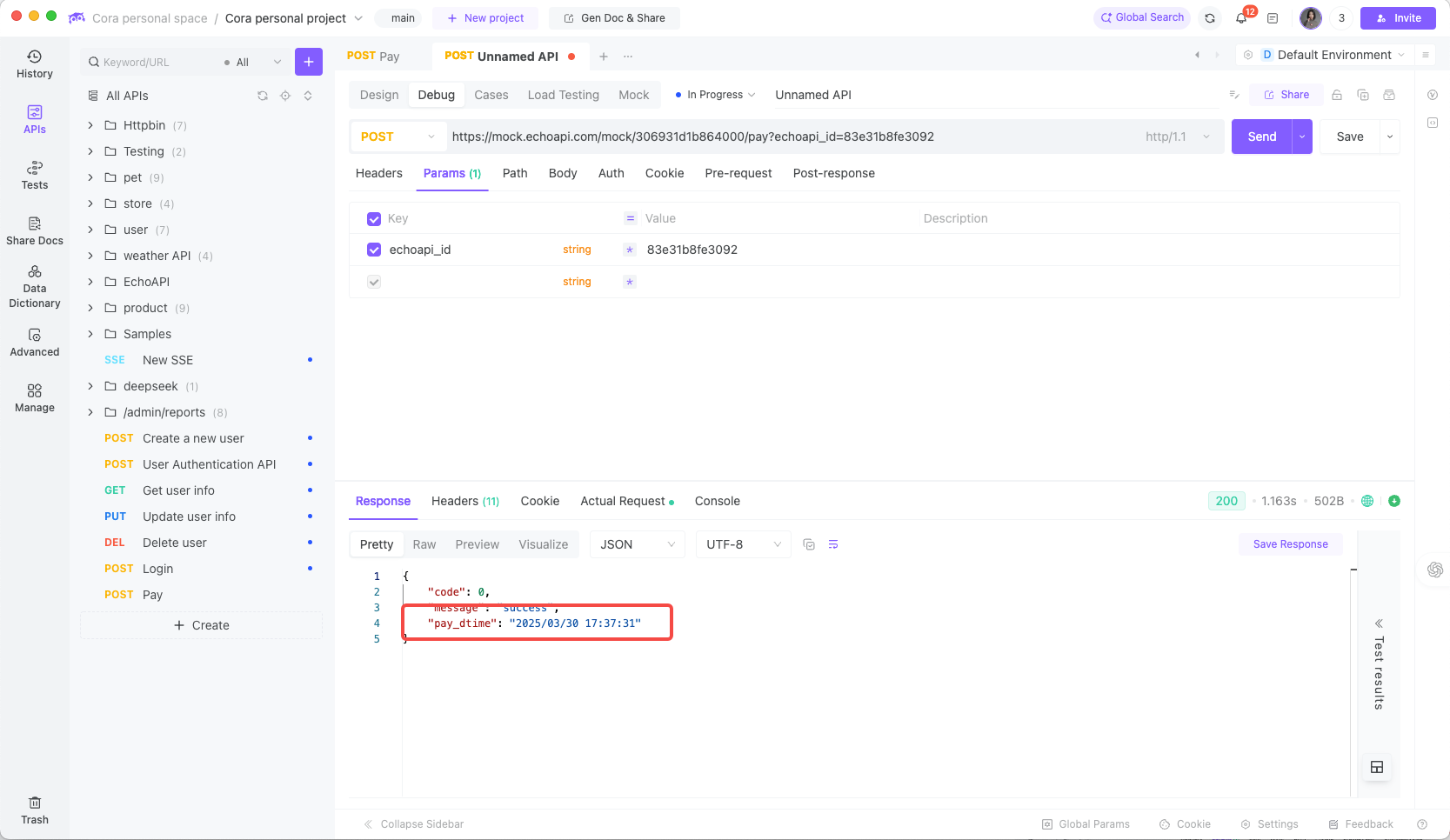
Now each request returns fresh data, avoiding static JSON limitations.
3.3 Third Mock Capability of EchoAPI: Custom Functions
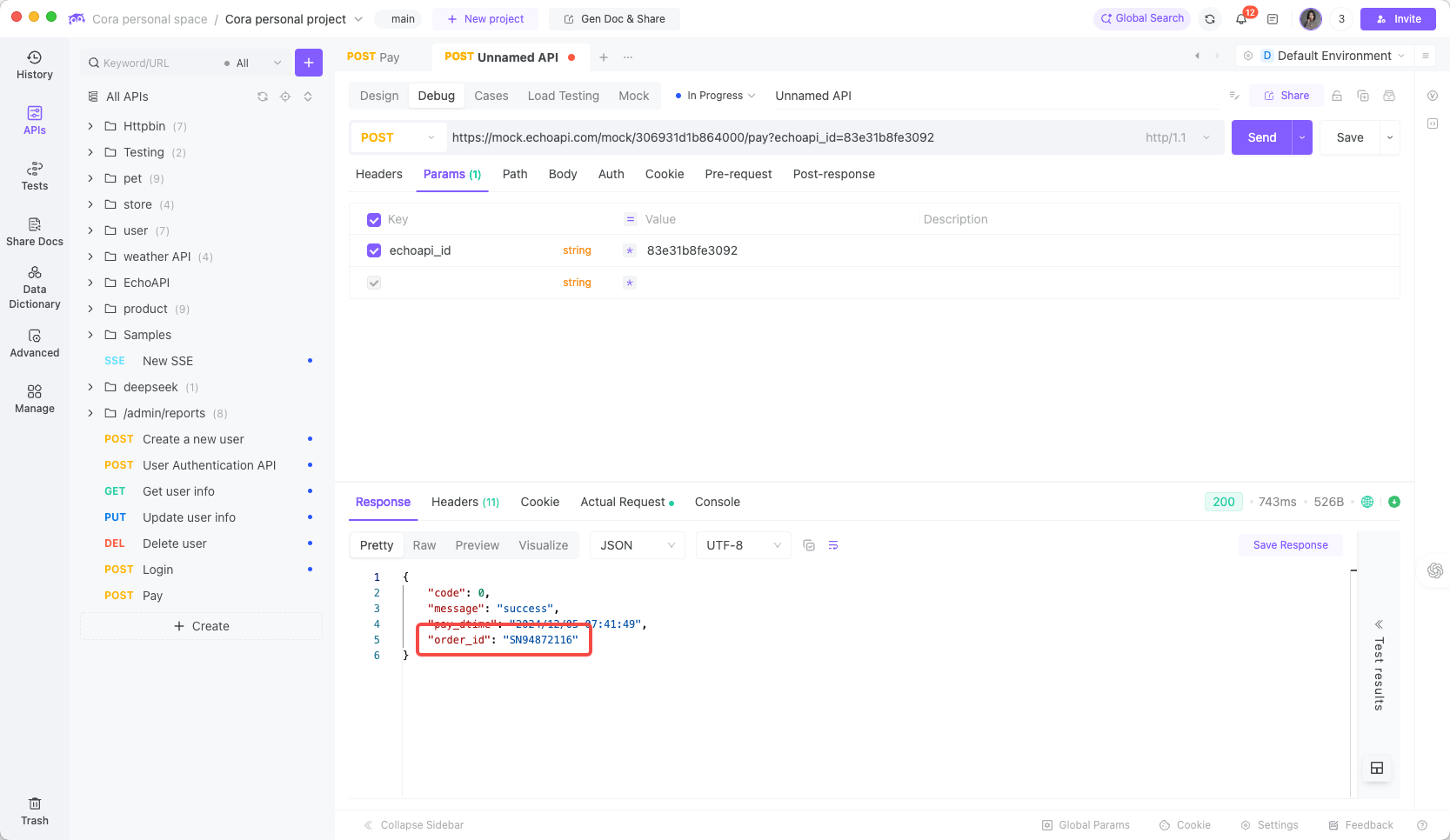
When built-in variables aren't sufficient, custom functions can implement complex logic. For example, adding an order_id field that must start with "sn" followed by 8 digits – a highly customized requirement:
{
"data": {
"code": 0,
"message": "success",
"pay_dtime":"2025-08-10 10:00:00",
"order_id":"sn12345678"
}
}
Use EchoAPI’s custom function as shown:
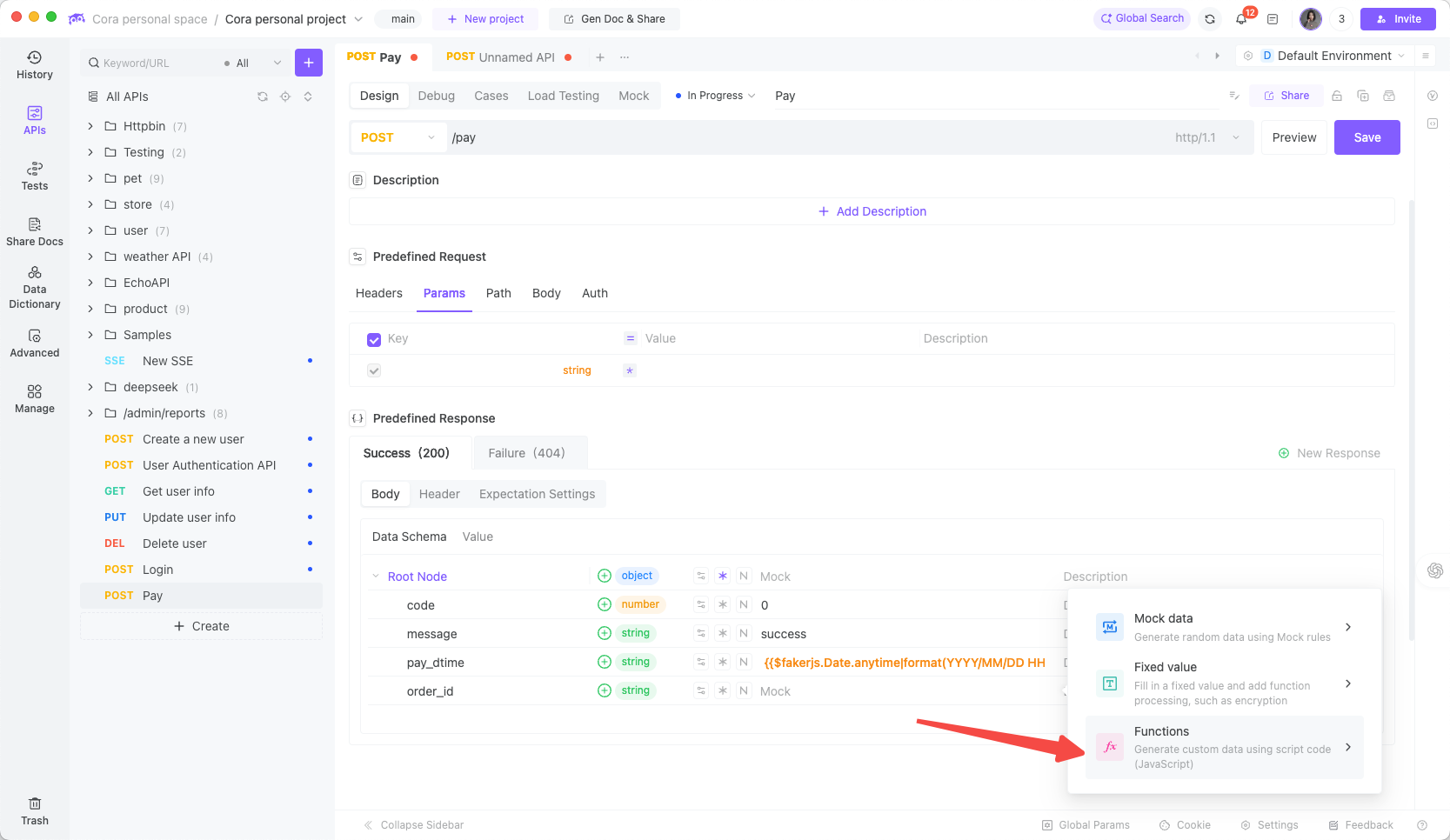
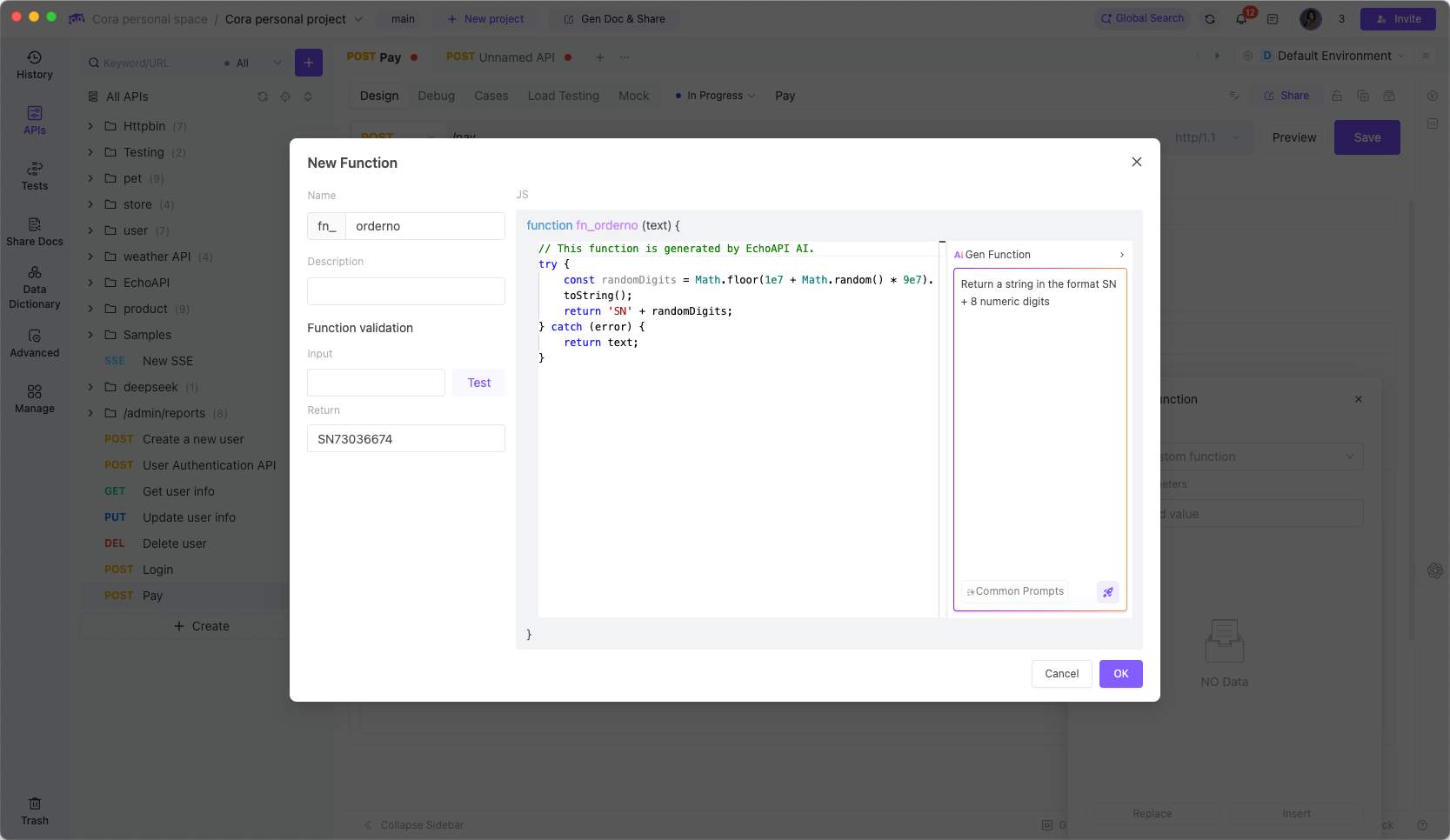
Create a new function fn_orderno using either EchoAPI's built-in AI capabilities or by manually writing an order number generation function:
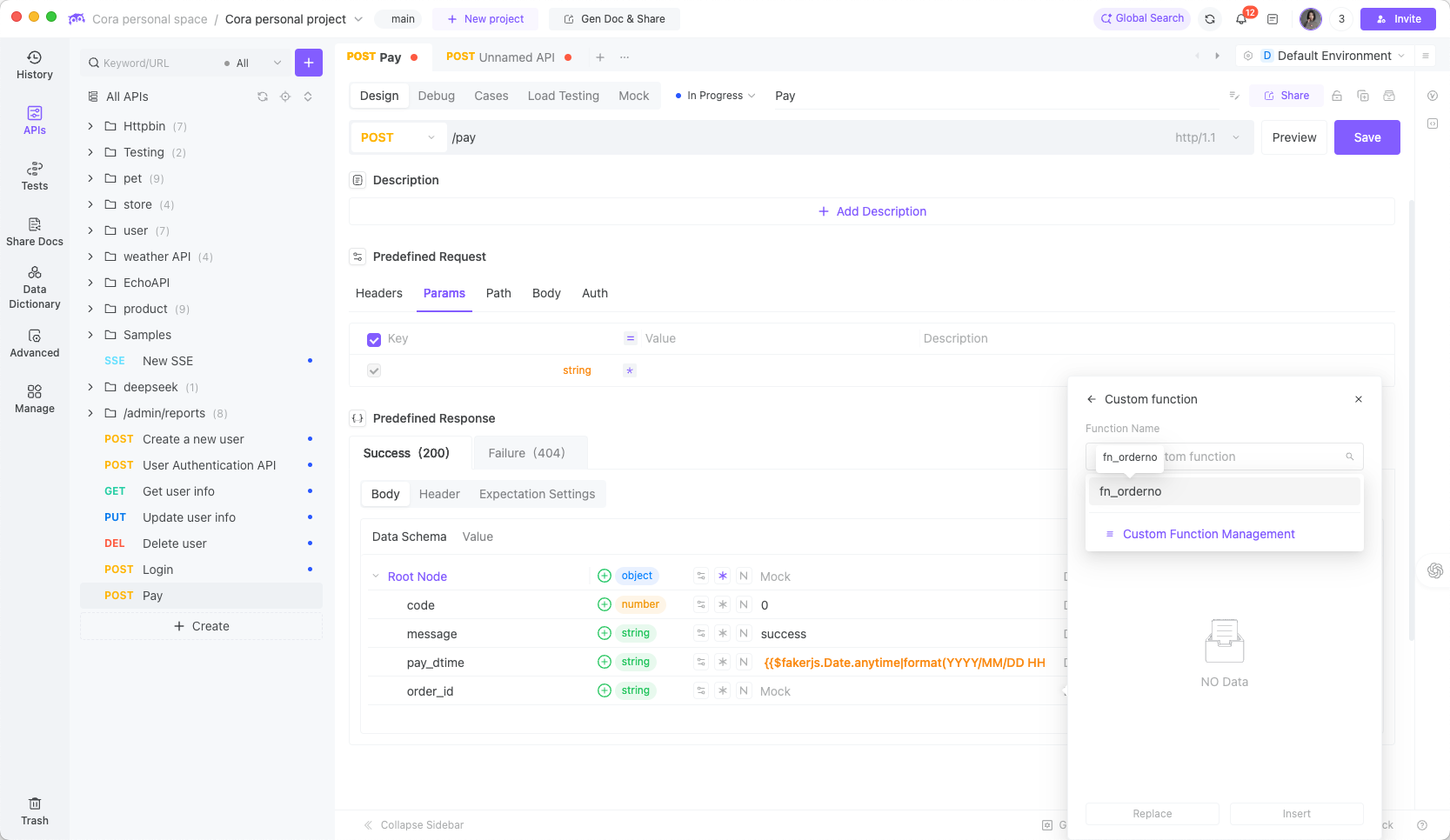
Response example:
3.4 Fourth Mock Capability of EchoAPI:Returning Different Responses Based on Request Parameters
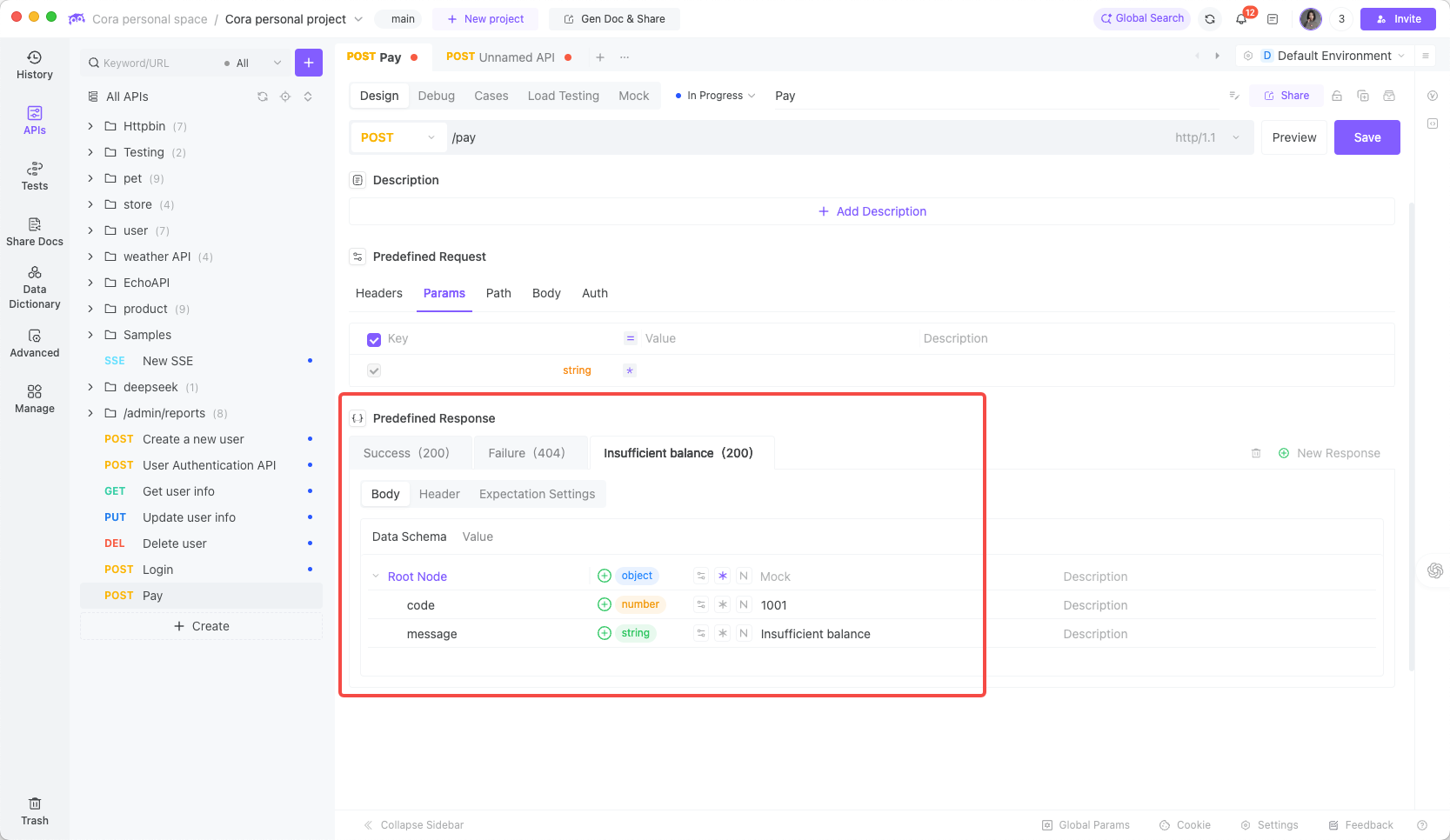
Payment functionality needs to handle scenarios like successful payment, insufficient balance, and account locked.
Create a new "Insufficient Balance" expectation and configure the relevant return parameters:
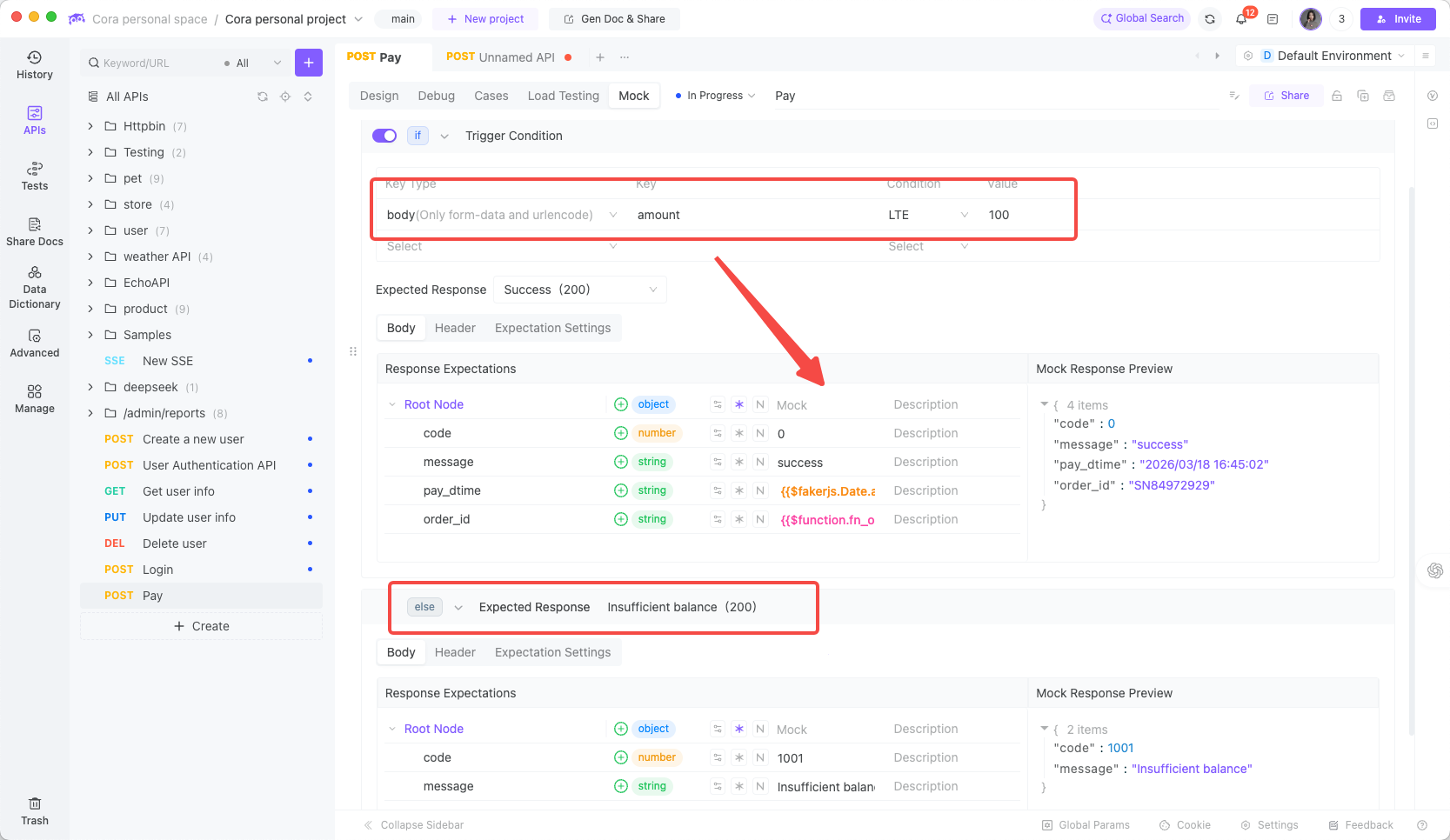
Returned response:
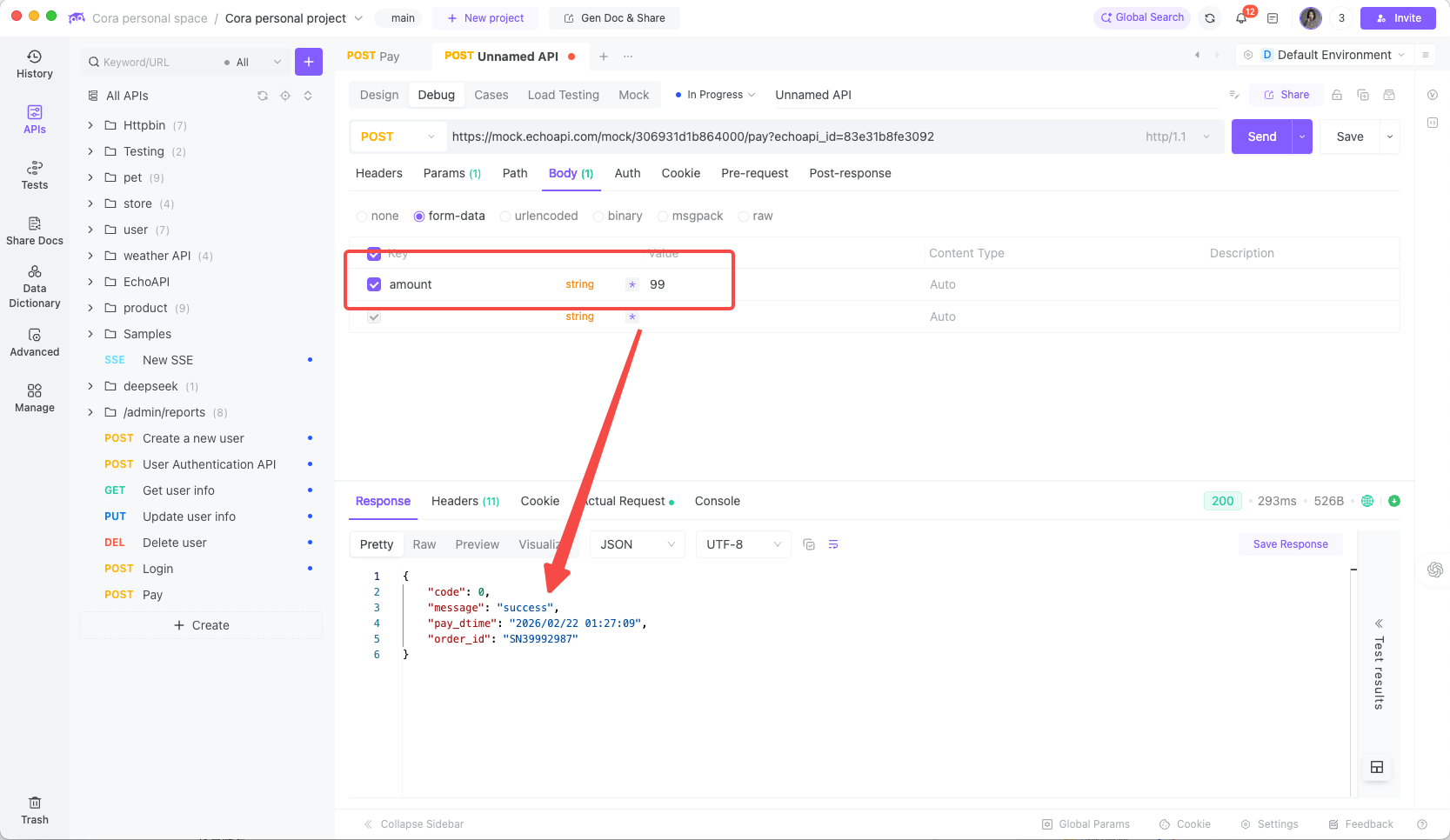
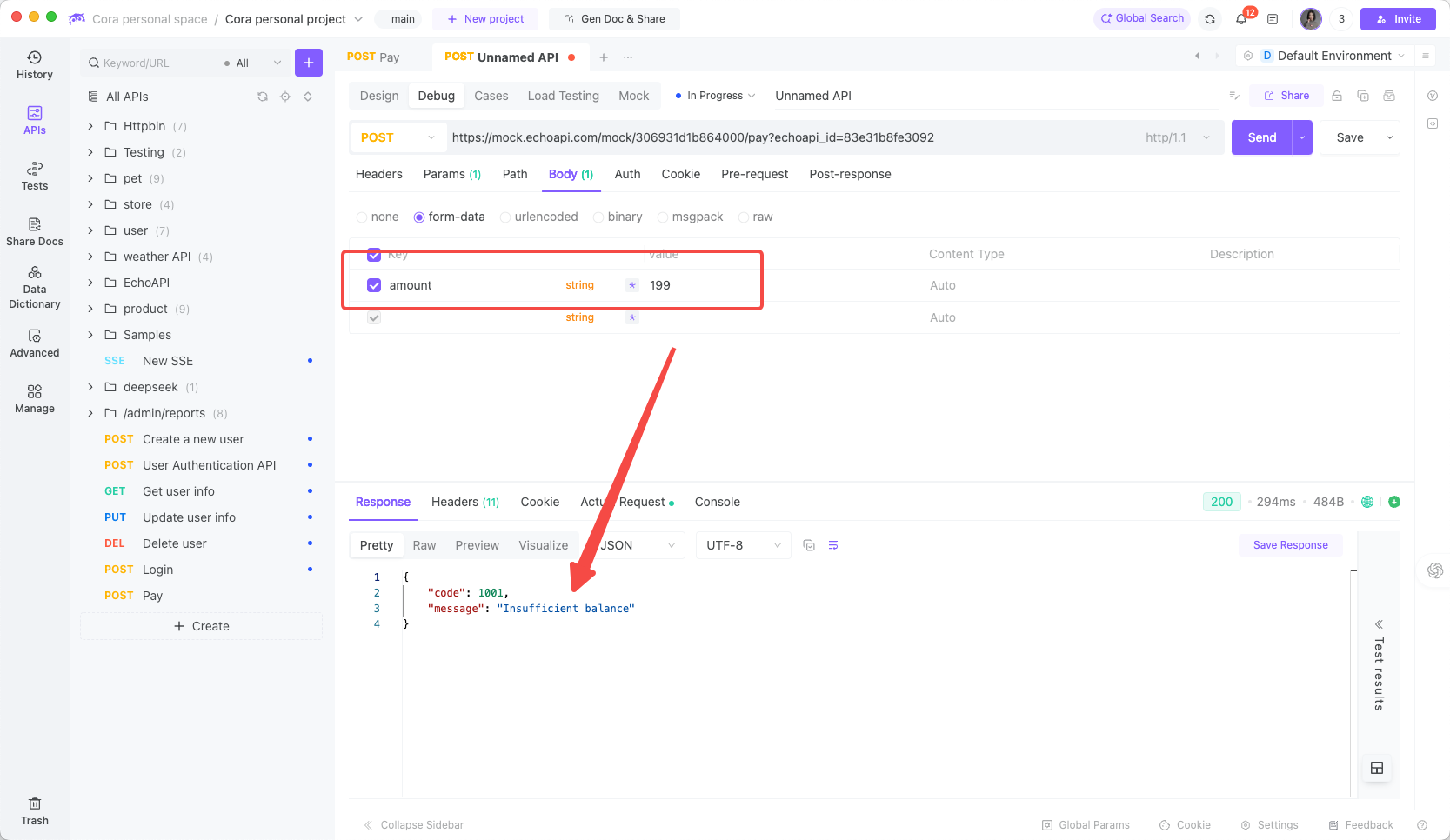
This approach is far closer to real-world behavior than static JSON.
4. Summary
Mocking isn't just an "optional" tool in frontend development – it's a core capability that significantly improves development efficiency.
This means:
- Frontend teams can develop independently without relying on backend interface completion.
- QA can reuse mock endpoints for early integration testing even when APIs aren't ready.
EchoAPI Advantages:
EchoAPI's mocking features provide a more modern solution with:
- Built-in variables: generate diverse data quickly.
- Custom functions: implement complex business logic, AI-assisted if needed.
Whether you need rapid iteration, independent development, or realistic scenario simulation, EchoAPI delivers a flexible, professional, and time-saving solution that keeps your projects moving forward seamlessly.
Happy Coding!




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server








