From Script Chaos to AI-Powered Efficiency: How EchoAPI Transforms Dynamic Variable Generation in API Testing
EchoAPI's AI-powered function generation transforms dynamic variable creation in API testing, eliminating manual scripting chaos and enabling business-logic-driven automation with natural language.
During our team’s journey toward automated testing for microservices APIs, we ran into a persistent challenge: in many test cases, we needed to dynamically generate user phone numbers that followed specific rules, UUIDs with business markers, and structured test email addresses.
The tool we were using—Postman—does offer some built-in variables like {{$guid}}, {{$timestamp}}, etc. But when it came to generating dynamic values that carried business-specific logic, it quickly fell short.
Traditionally, the workaround was for QA engineers to handwrite JavaScript functions in Pre-request scripts to fill in the gaps. But as the number of APIs and the complexity of rules grew, this approach spiraled into a maintenance nightmare. Things only improved once we introduced EchoAPI and leveraged its AI-powered function generation capability.
The Value and Limits of Postman’s Built-in Variables
Postman’s preset variables are convenient for quick testing. Some typical examples include:
{{$guid}} // Auto-generate a UUID v4
{{$timestamp}} // Current timestamp (seconds)
{{$randomInt}} // Random integer
{{$randomEmail}} // Random email address
{{$randomBoolean}} // true/false random value
The upside is obvious: they’re plug-and-play, requiring zero scripting.
But the limitations are equally clear:
- They don’t support business customization, such as generating phone numbers that match specific regex rules, or usernames like
user_20250625_random6digits. - They’re limited in type and cannot be combined.
- They don’t support logical branching or integration with API context.
For example, to generate a valid phone number that starts with '212', '513', or '917', you’d need to write a Pre-request script in Postman:
// Manual script
function randomPhone() {
const prefix = ['212', '513', '917'][Math.floor(Math.random() * 3)];
const suffix = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1e8).toString().padStart(8, '0');
return prefix + suffix;
}
This introduces two major problems:
- If dozens of APIs rely on the same token, you’re forced to duplicate the script everywhere—an unmaintainable mess when many custom values are involved.
- Most QA engineers aren’t comfortable writing JavaScript, which blocks test development.
The Practical Value of EchoAPI’s AI Function Generation
EchoAPI not only supports all of Postman’s built-in variables but also goes further with a breakthrough feature: AI-generated functions.
Its key capability: turn a natural language request into a reusable JavaScript function—making custom dynamic variables virtually effortless.
Example 1: Auto-generating Phone Numbers
Requirement: generate a digit number starting with 212, 646, or 917.
In Postman, you’d write:
// Manual script
function randomPhone() {
const prefix = ['212', '646', '917'][Math.floor(Math.random() * 3)];
const suffix = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1e8).toString().padStart(7, '0');
return prefix + suffix;
}
With EchoAPI, all you do is click Insert Dynamic Value → Custom Function, then describe your need in plain language:
“Generate a phone number starting with 212, 646, or 917.”
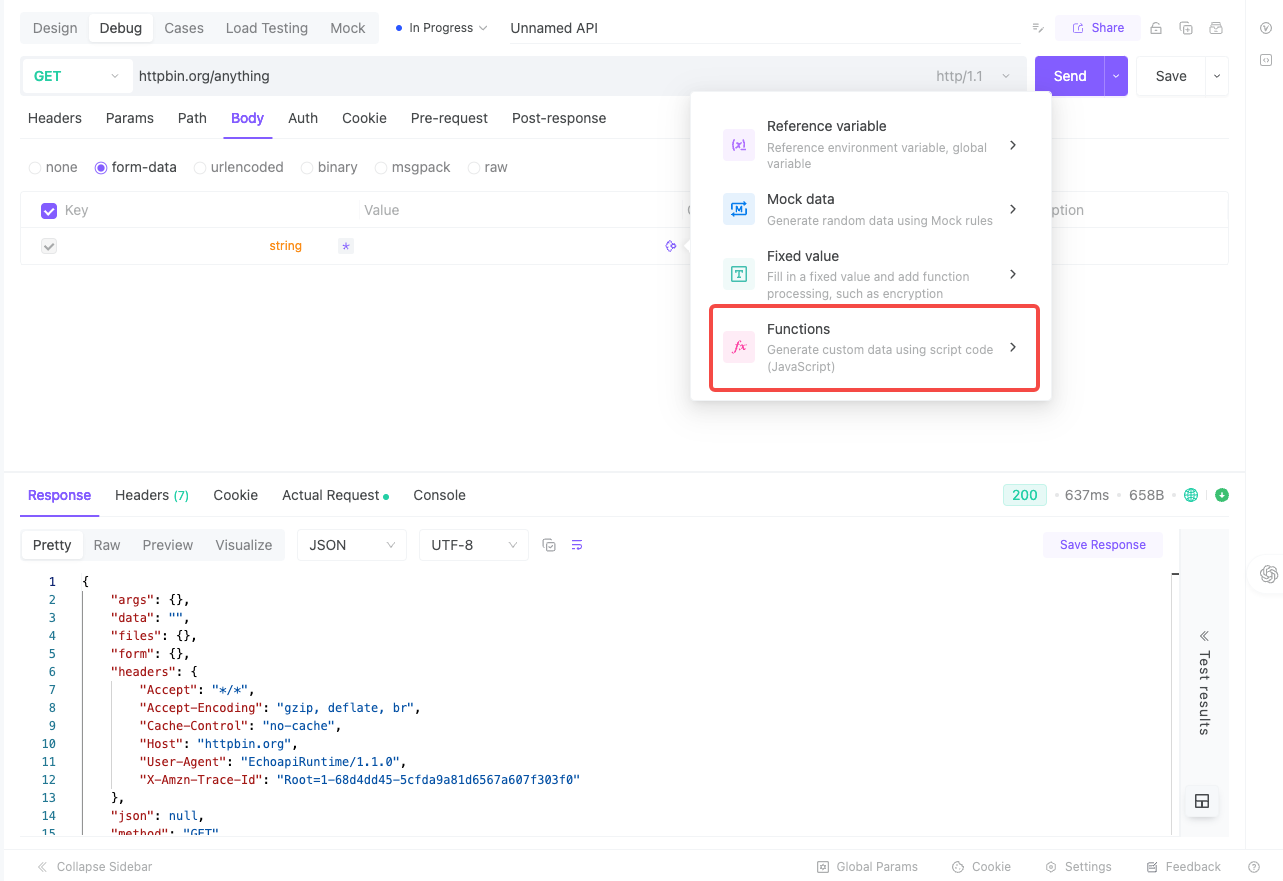
EchoAPI instantly generates the function and registers it as {{$function.fn_getMobile()}}, ready to use in any API request—no duplication, no maintenance headache.
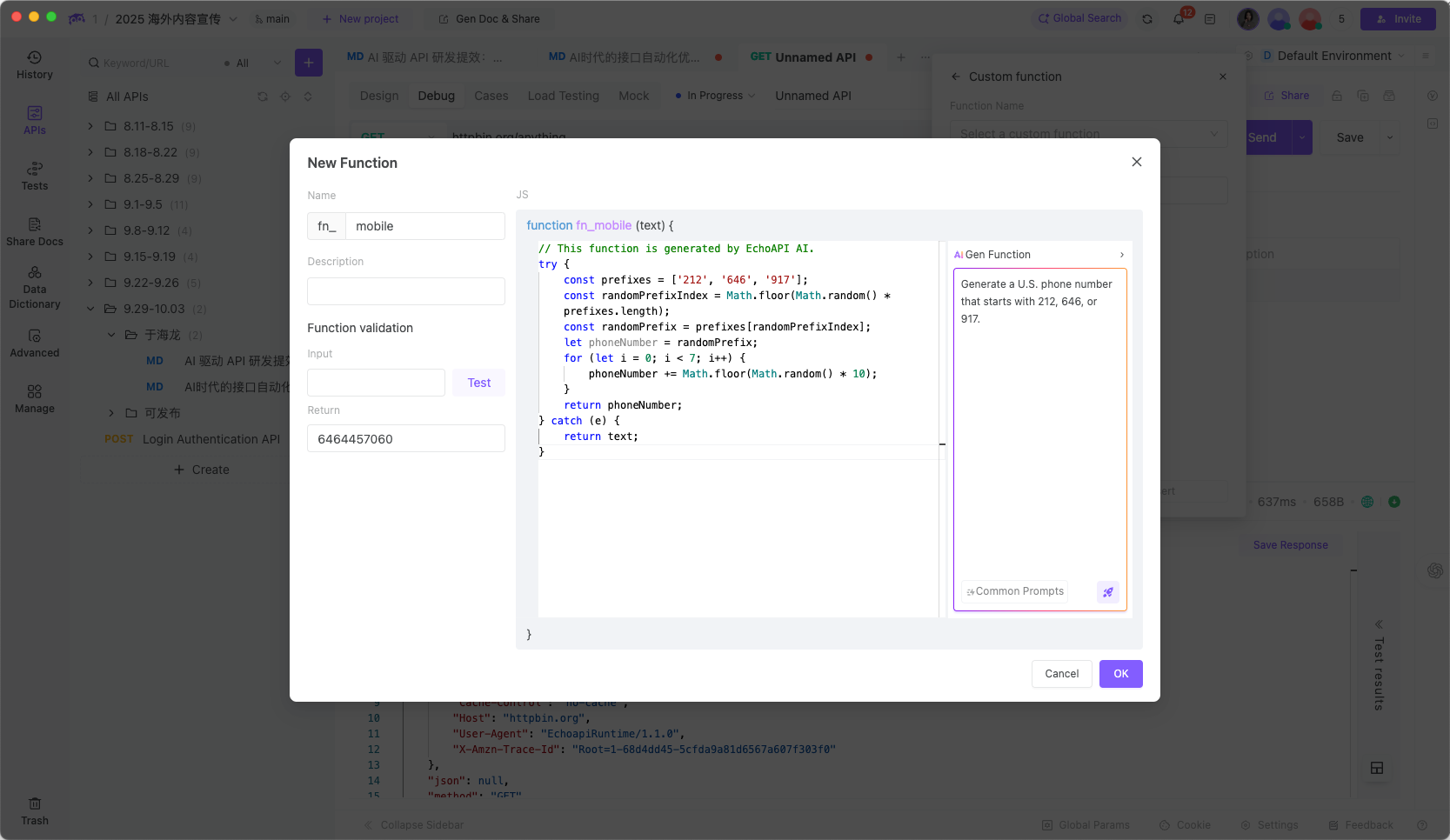
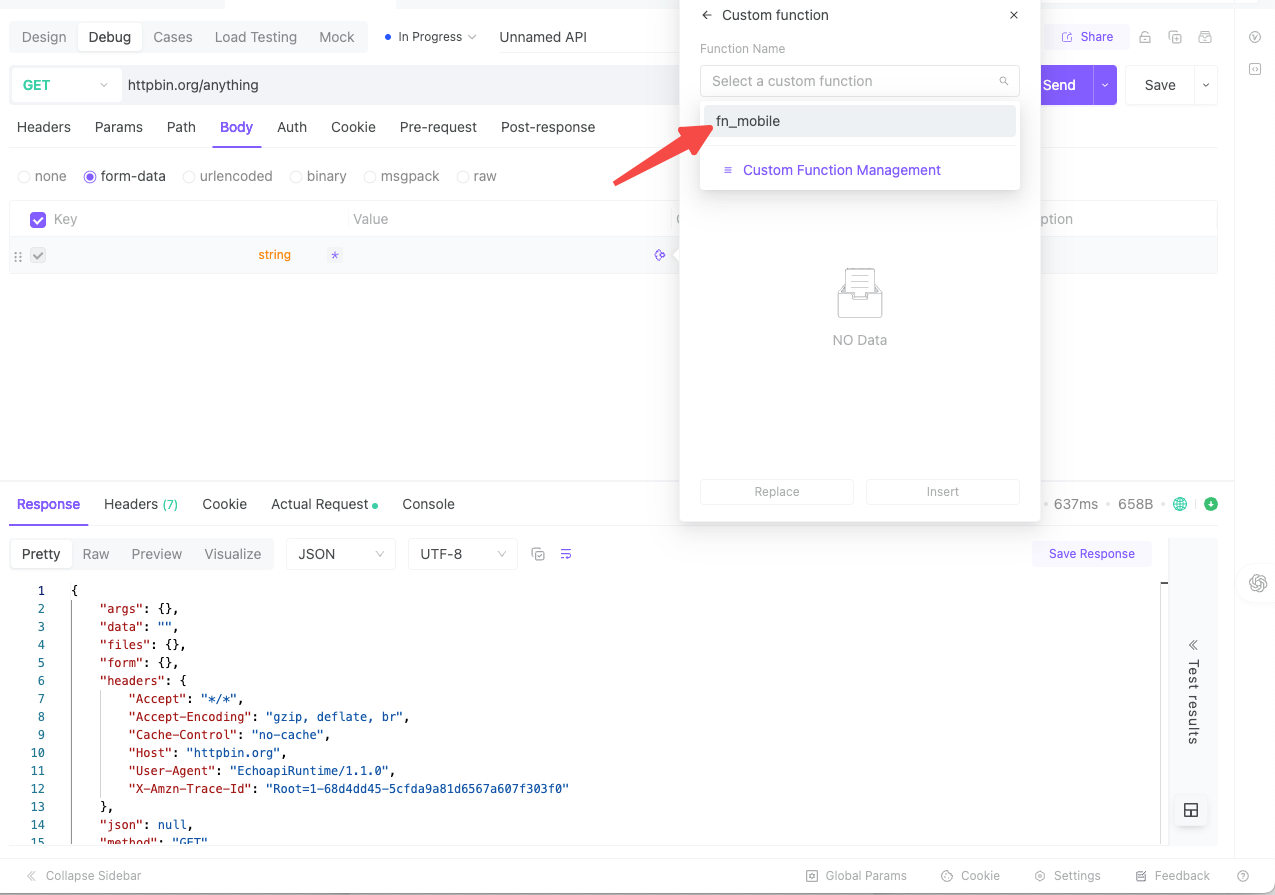
Once created, you simply select and apply it wherever needed:
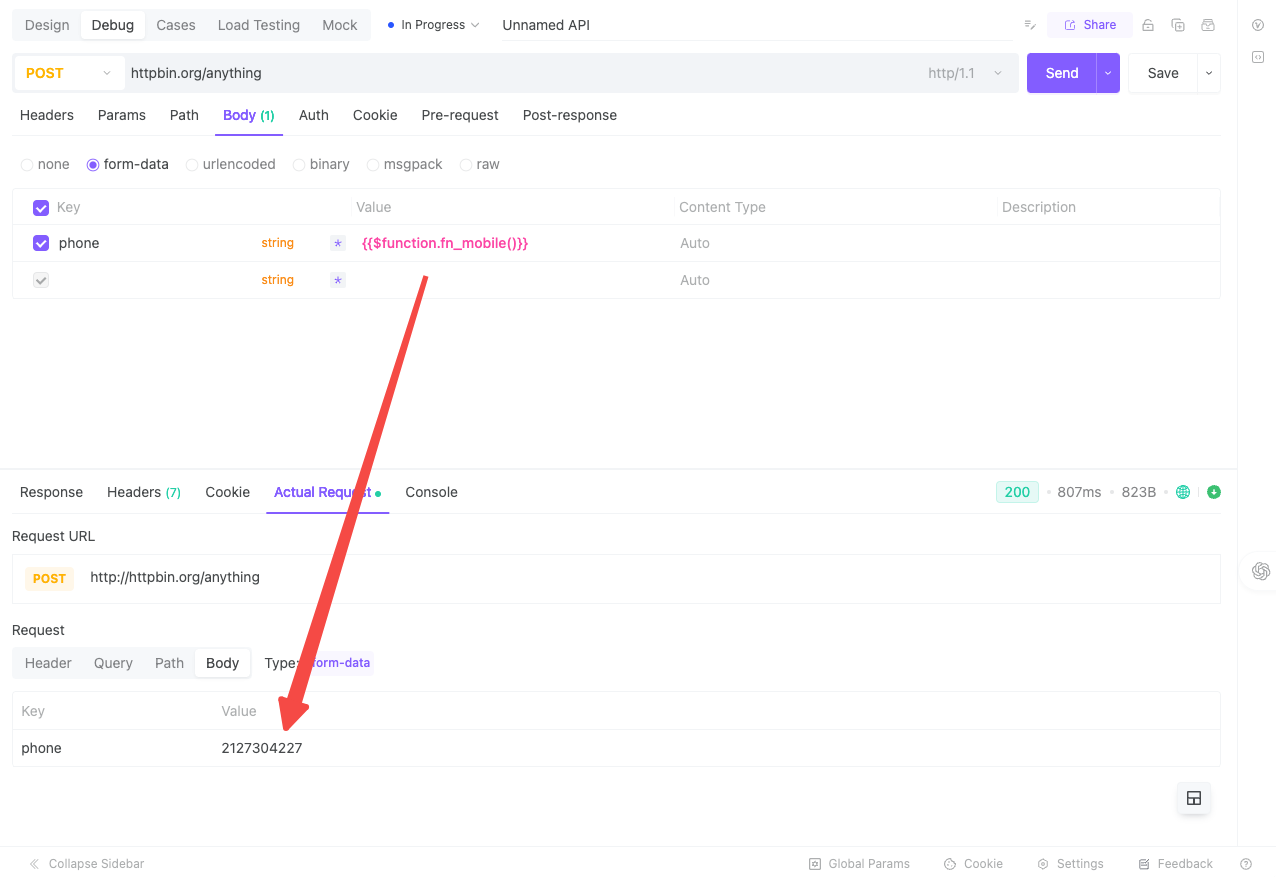
Example 2: Custom Email Addresses
Requirement: generate an email like test_<timestamp>@company.com.
In Postman, you’d write:
const email = `test_${Date.now()}@company.com`;
pm.environment.set("custom_email", email);
With EchoAPI, just describe it:
“Generate an email with prefix test_ + current timestamp, and domain company.com.”
The system generates and registers a reusable function automatically—same process as with the phone number example.
Architectural Comparison: Postman vs. EchoAPI
| Feature | Postman | EchoAPI |
|---|---|---|
| Built-in variables | ✅ Fixed set | ✅ Fully compatible with Postman |
| Custom logic | ✅ Manual scripts only | ✅ Scripts or AI-generated functions |
| Function generation | ❌ Not supported | ✅ AI-powered, natural language → code |
| Maintainability | ❌ Duplicate scripts, hard to track | ✅ Centralized, reusable functions |
| Scalability | ❌ Limited | ✅ Adaptable to any business scenario |
For backend and QA engineers, this extensibility means:
- When business rules change, only the function definition needs updating—not every script.
- Dynamic variables can be logically encapsulated, keeping APIs clean and scripts controllable.
- AI-generated code is high-quality and low-bug, boosting both efficiency and reliability.
- The boundary between human input and automation becomes clearer, reducing manual overhead.
Conclusion: Don’t Let Tool Limits Become Workflow Bottlenecks
From both a development and testing perspective, it’s not just about whether an API “works.” It’s about sustainable workflows, manageable maintenance costs, and clear separation from business logic.
Postman’s preset variables help with simple randomness, but the ceiling is low—once you hit business complexity, script sprawl becomes inevitable.
EchoAPI’s AI-generated functions unlock a low-barrier, highly extensible alternative. Dynamic variables evolve from a fixed, tool-provided set into reusable testing assets.

For anyone who has built large-scale API testing platforms, this isn’t just a feature upgrade—it’s a methodological leap, solving the root problem of “repetition, inefficiency, and lack of control.”




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server









