EchoAPI’s Powerful Dynamic Values & Custom Functions
EchoAPI's Dynamic Values and Custom Functions streamline API testing by automating dynamic parameters and complex logic. They eliminate manual errors and accelerate debugging, especially for multi-step workflows and regional compliance.
Dynamic values and custom functions are key features in EchoAPI that streamline API testing and adapt to complex business logic.
They shine in multi-step workflows, parameter dependencies, and cases requiring flexibility.
Let’s break it down with real-world scenarios.
Dynamic Values: Handle Parameters That Change With Context
Dynamic values are parameters automatically generated or retrieved in real time (e.g., timestamps, random numbers, values from previous responses).
They solve two core problems: parameters that change constantly and dependencies between APIs.
Example: E-commerce Checkout Flow (Cross-API Dependency)
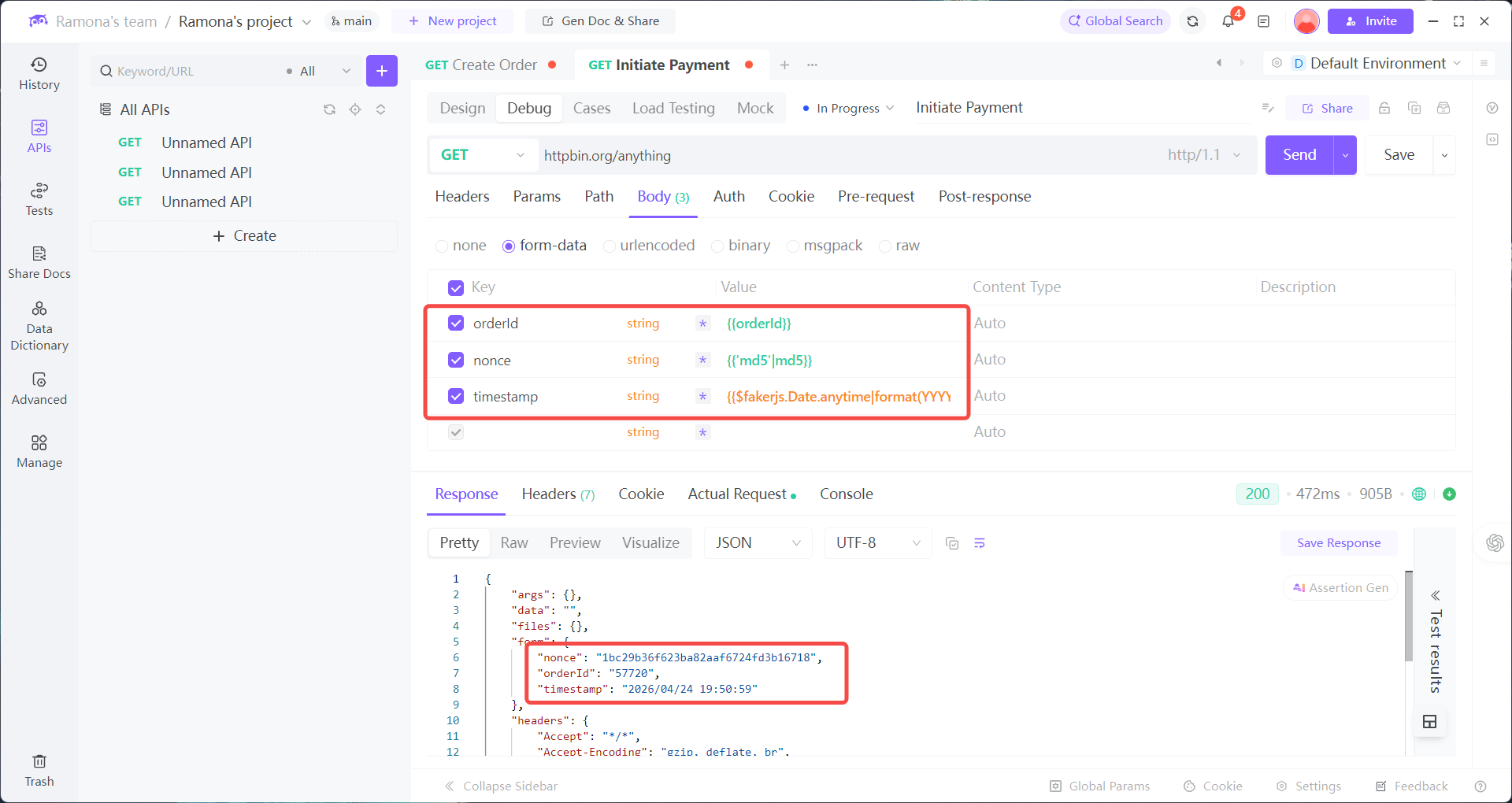
A US-based e-commerce developer needs to debug the chain: Create Order → Make Payment
1. Create Order API:
returns a unique orderId (new each time).
Save the returned orderId into env variables
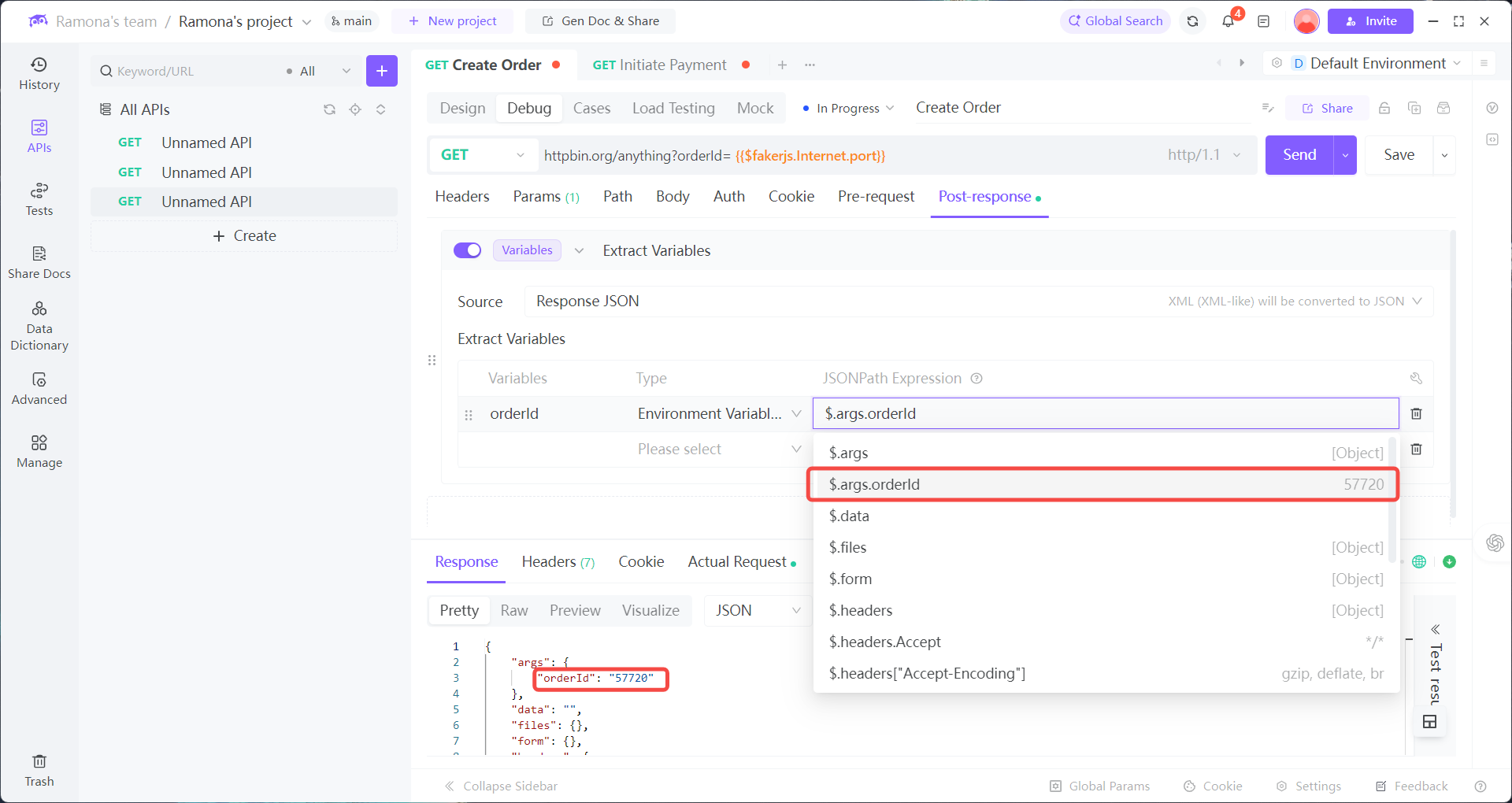
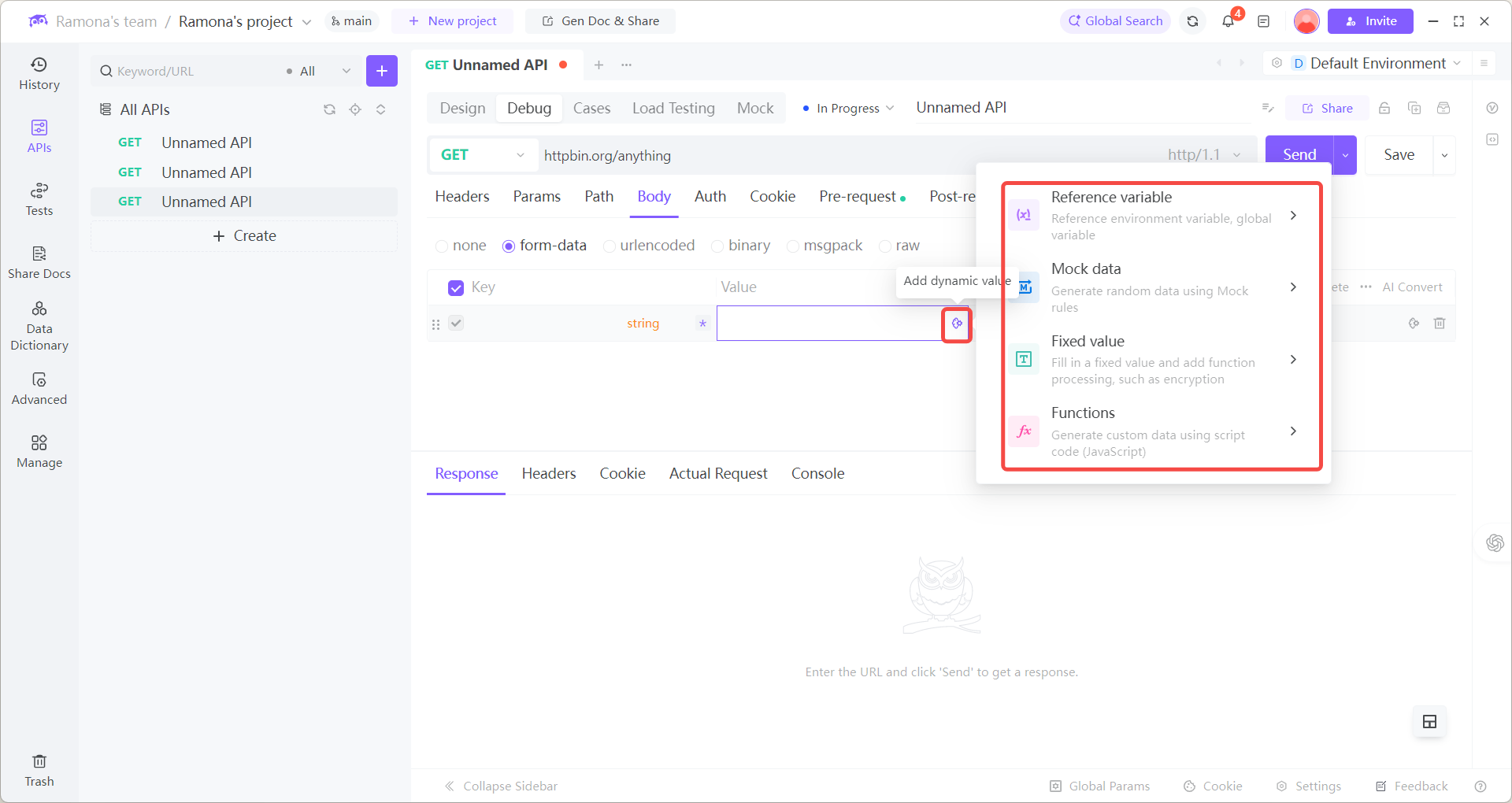
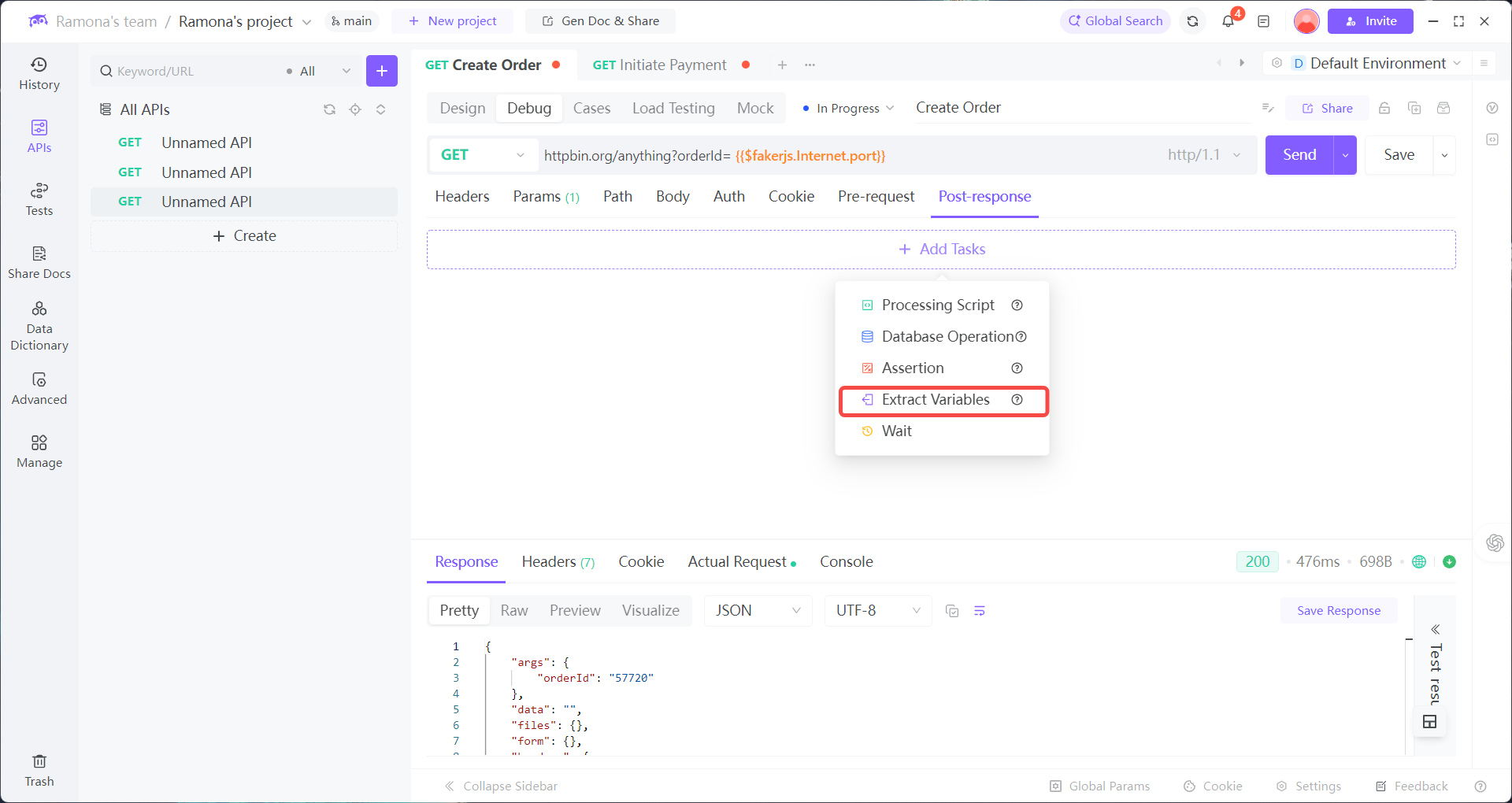
Add Post-response → Extract Variables
Send request → see random output
Pick a function → Insert
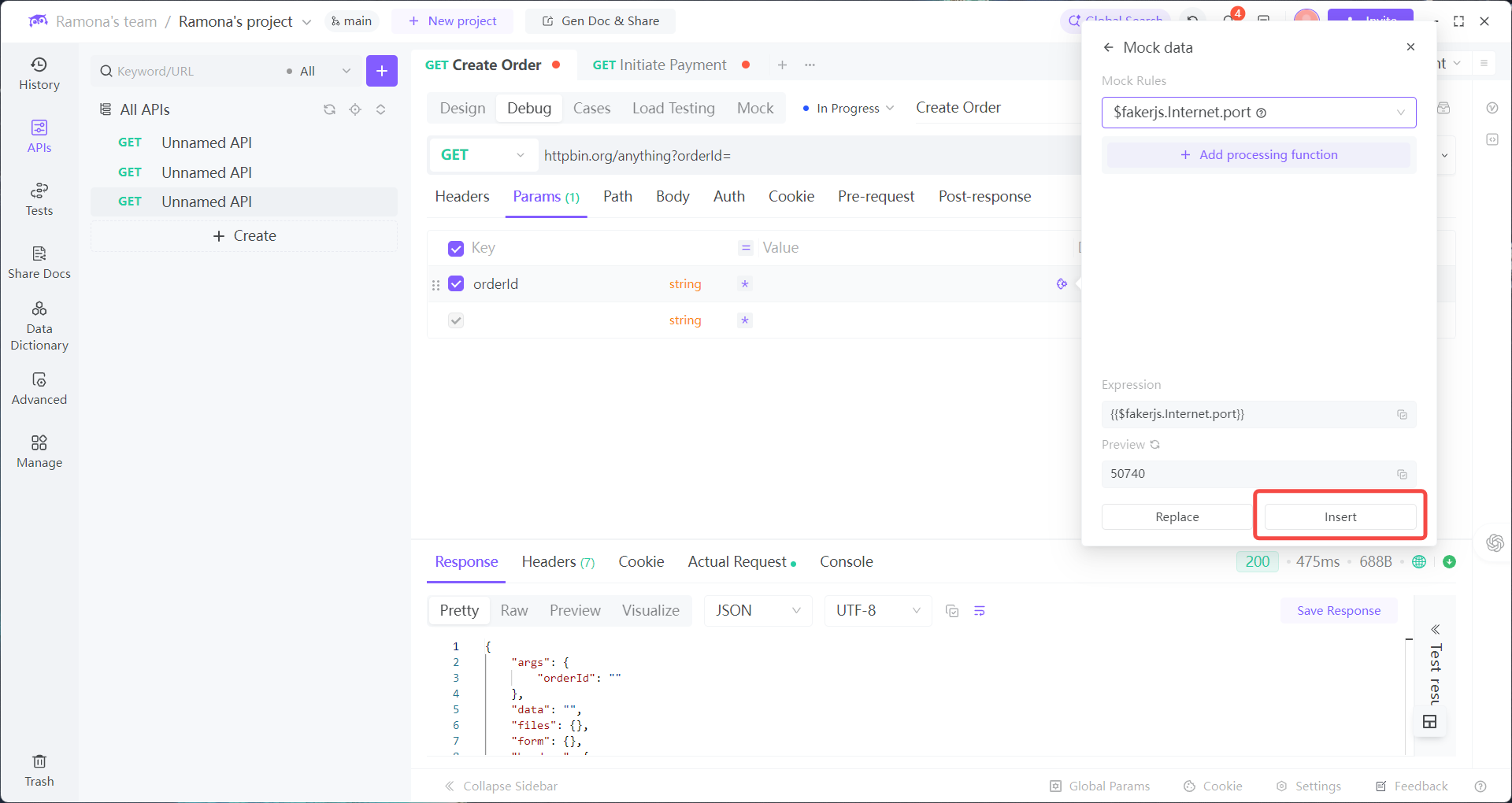
Click Mock data function
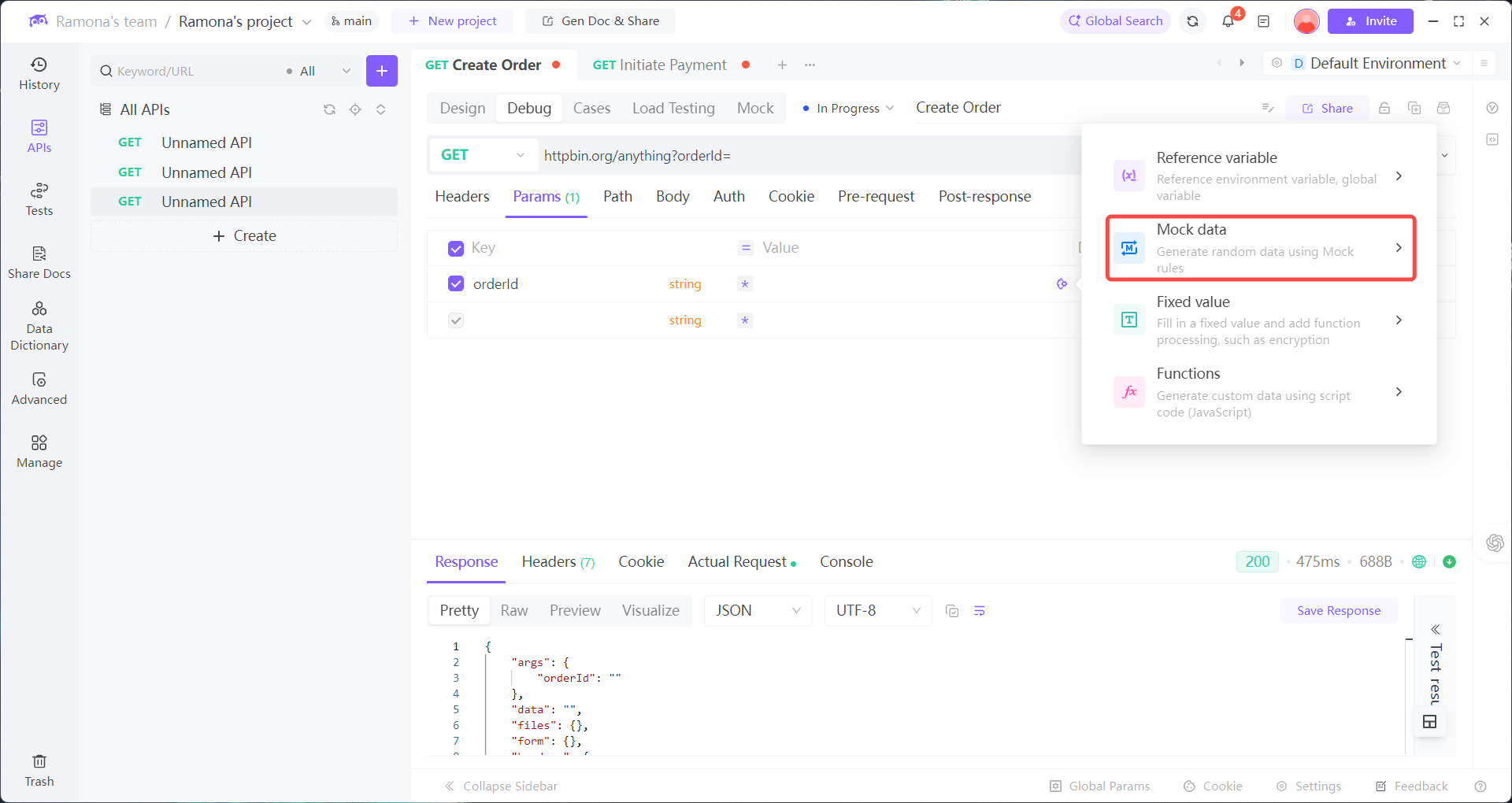
2. Payment API:
requires the orderId from the previous step, plus:
timestamp(to avoid expired requests)nonce(to prevent replay attacks)
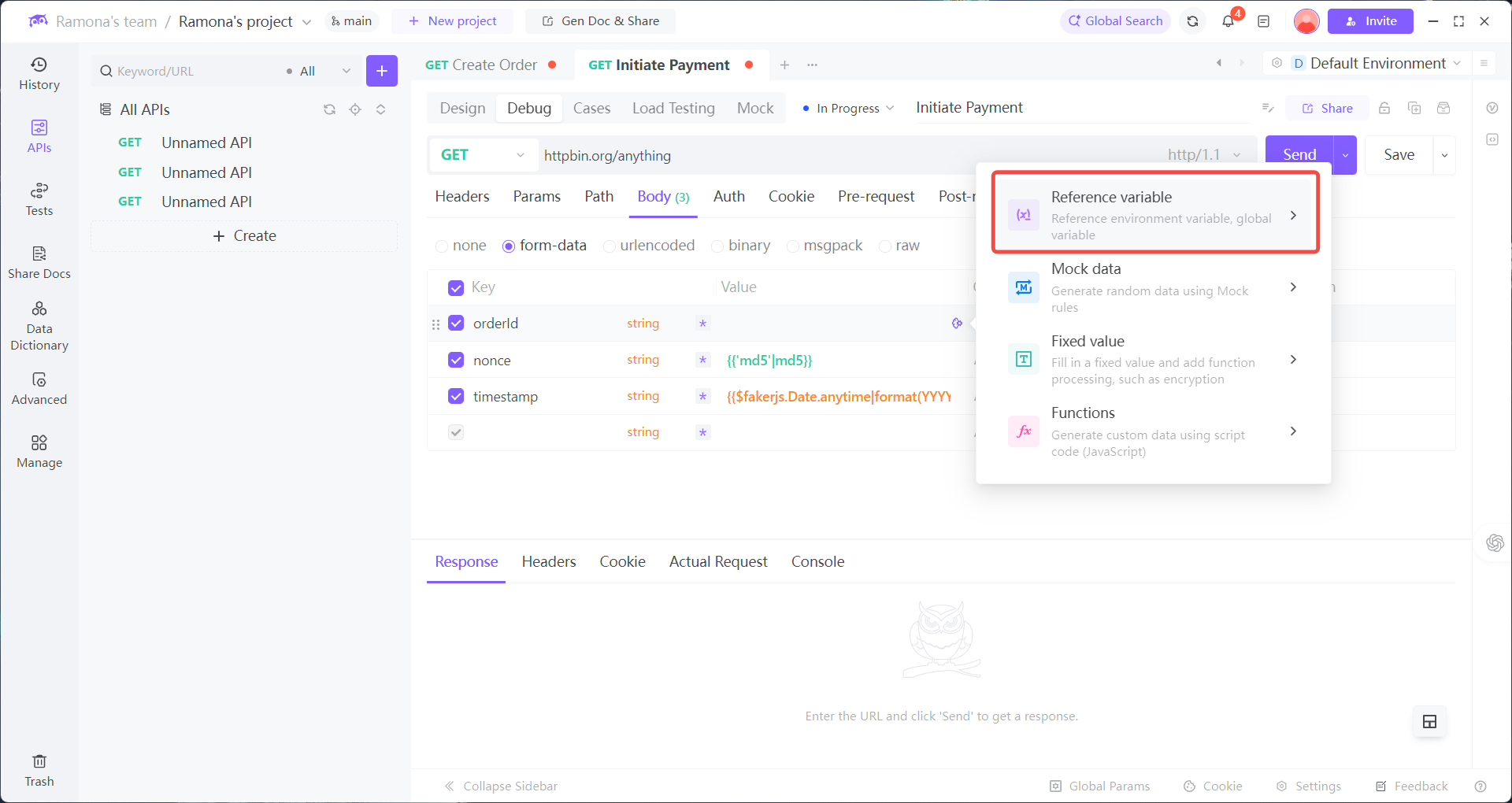
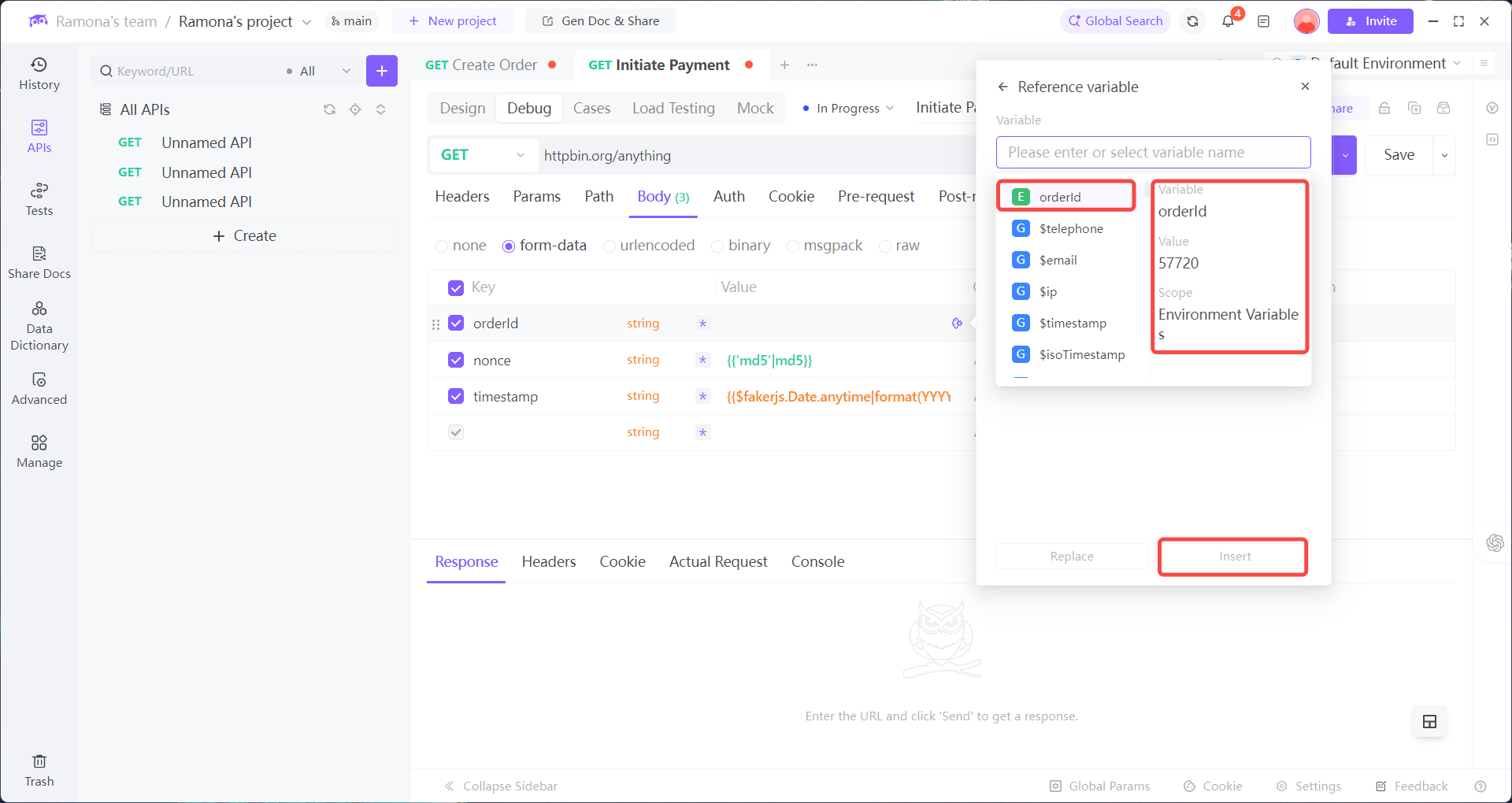
How to Apply Dynamic Values
1. After calling Create Order, use EchoAPI’s Post-response → Extract Variables to auto-extract orderId and store it in the environment.
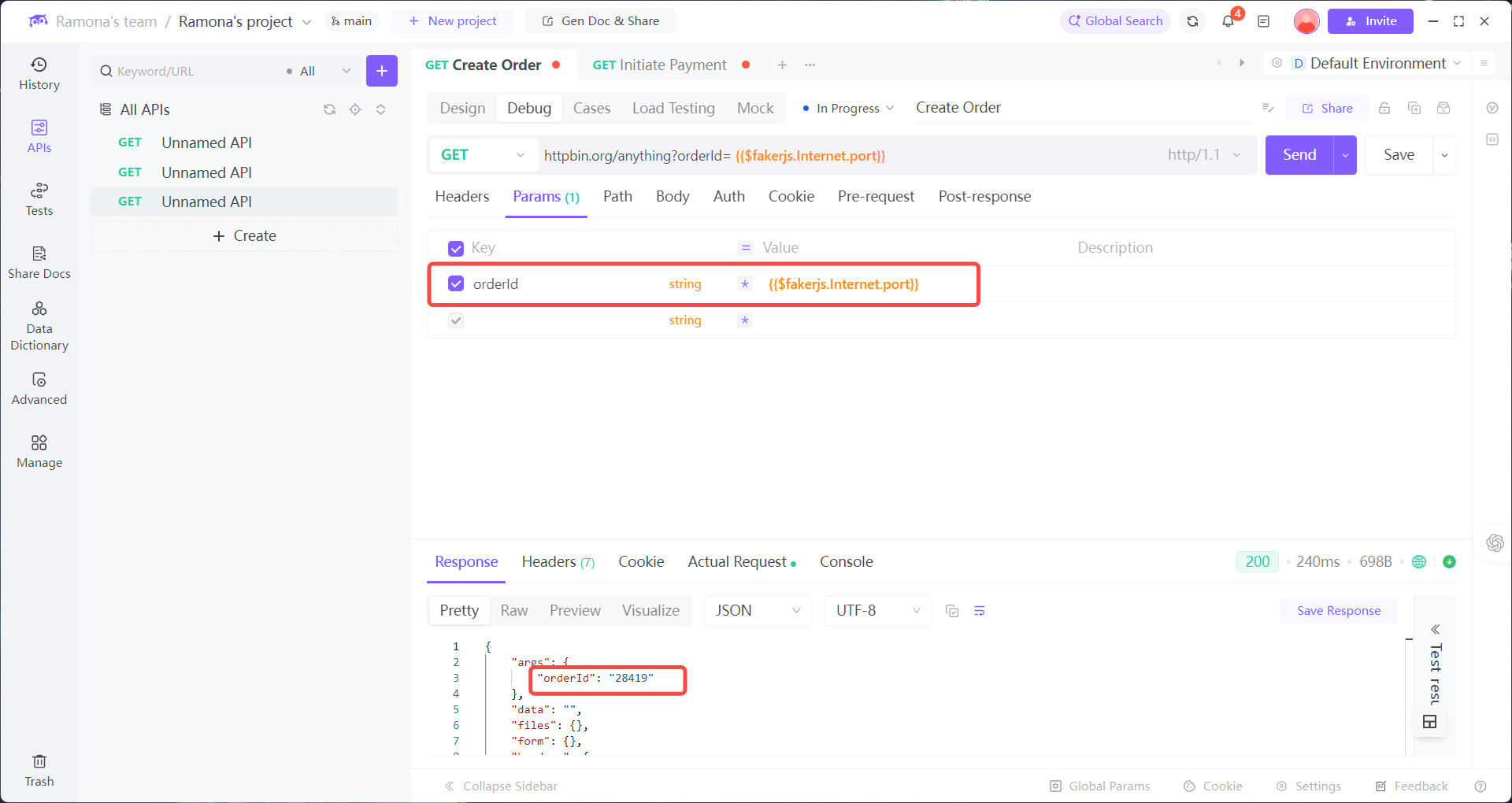
2. When calling Payment API, select dynamic values in parameters:
orderId: Reference Env →orderIdtimestamp: Add Dynamic Value → Mokc Data → Date (auto-generated in ms)nonce: Add Dynamic Value → Mokc Data → Random String (auto-generated, valid format)
Key Benefits
- No copy-paste errors: No need to manually copy IDs or calculate timestamps. Avoids typos that break requests.
- Faster debugging: Multi-API chains that used to take 5 minutes manually can now be done in under 1 minute.
- Time zone ready: Auto-generate UTC and regional times (JST, PST, WIB, etc.) without manual conversion — perfect for global testing.
Built-In System Dynamic Values
EchoAPI comes with ready-to-use dynamic values that don’t require any setup.
They generate data on the fly and cover the most common needs for API testing.
Time-Based Dynamic Values
Time values are among the most frequently used. Perfect for APIs that require timestamps or date-based validation. Built-in support for multiple time zones.
| Value Type | Example | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unix Timestamp (ms) | 1620000000000 | Milliseconds since 1970-01-01 UTC | Replay attack prevention, request marker |
| Unix Timestamp (s) | 1620000000 | Seconds since 1970-01-01 UTC | APIs that expect seconds-based format |
| UTC Time String | 2023-06-15T12:00:00Z | Standard UTC ISO8601 with zone | International APIs |
| Local Time String | 2023-06-15 20:00:00 | Current system time zone | Localized systems |
| Japan Time (JST) | 2023-06-15 21:00:00 | UTC+9 | Japan region testing |
| Indonesia Time (WIB) | 2023-06-15 19:00:00 | UTC+7 | Indonesia region testing |
| US West (PST/PDT) | 2023-06-15 05:00:00 | Pacific Time | US West Coast APIs |
| Date Only (YYYY-MM-DD) | 2023-06-15 | Year-Month-Day only | Date queries |
| Relative Time | Now + 1h | Supports time offsets | Expiry settings (e.g. token) |
Advantage: No manual time-zone math. Critical for global APIs where accuracy across regions matters.
Random Dynamic Values
Random values generate unpredictable data, commonly used for replay-attack prevention and test data generation.
| Value Type | Example | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Integer | 12345 | Range can be set (e.g., 1000–9999) | Generate test IDs |
| Random String | x7Bp9Q | Custom length/charset (digits, letters, symbols) | Nonce for replay prevention |
| Random UUID | f47ac10b-58cc-4372-a567-0e02b2c3d479 | Standard UUID v4 | Unique identifier |
| Random Boolean | true / false | Randomly returns true/false | Test conditional logic |
| Random Email | test_123@example.com | Valid email format | Generate test user accounts |
| Random Phone | +12065551234 | Supports country codes (US, JP, ID, etc.) | Test phone input |
| Random IP | 192.168.0.1 | Valid IP format | Simulate requests from different IPs |
Advantage: Define rules to generate realistic test data — no need to craft it manually.
Environment Info Dynamic Values
These values pull information from the current test environment, useful for identifying request sources or context.
| Value Type | Example | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current Project ID | proj_123456 | Unique identifier of active project | API audit logs |
| Current Environment | production | Active environment (dev/test/prod) | Env-specific logic |
| Local IP | 192.168.0.1 | IP of local machine | APIs bound to IP |
| Local Hostname | my-laptop | Hostname of local machine | Device identification |
| EchoAPI Version | 2.3.0 | Installed EchoAPI version | Version compatibility testing |
| OS | Windows 10 / macOS 12 | Operating system | OS-specific API behavior |
Advantage: Auto-fills environment data without manual lookup, ensuring accuracy.
Constants & Format Dynamic Values
Provides commonly used constants and format helpers to simplify parameter setup.
| Value Type | Example | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Null | null | Standard null value | Default for optional fields |
| Empty String | "" | Blank string | Params requiring empty string |
| Newline | \n | Line break escape | Multiline text fields |
| Tab | \t | Tab escape | Formatted text input |
| Space | (space) | Space character | Params needing separators |
| Empty JSON Object | {} | Blank JSON object | Params requiring empty object |
| Empty JSON Array | [] | Blank JSON array | Params requiring empty array |
Advantage: Standardized constants prevent formatting errors in requests.
Key Features of Built-in Dynamic Values
- Ready to use — no setup, works out of the box
- Real-time — generated fresh for each request
- Offline support — works without internet, fully local
- Cross-platform — same behavior in EchoAPI desktop, VS Code, and IDEA plugins
- Composable — can be combined with other dynamic values or custom functions
Example: generate an order ID with a timestamp prefix + UUID
ORDER_{{$fakerjs.Date.birthdate|format(YYYY/MM/DD HH:mm:ss,+08:00)}}{{$fakerjs.String.uuid}}
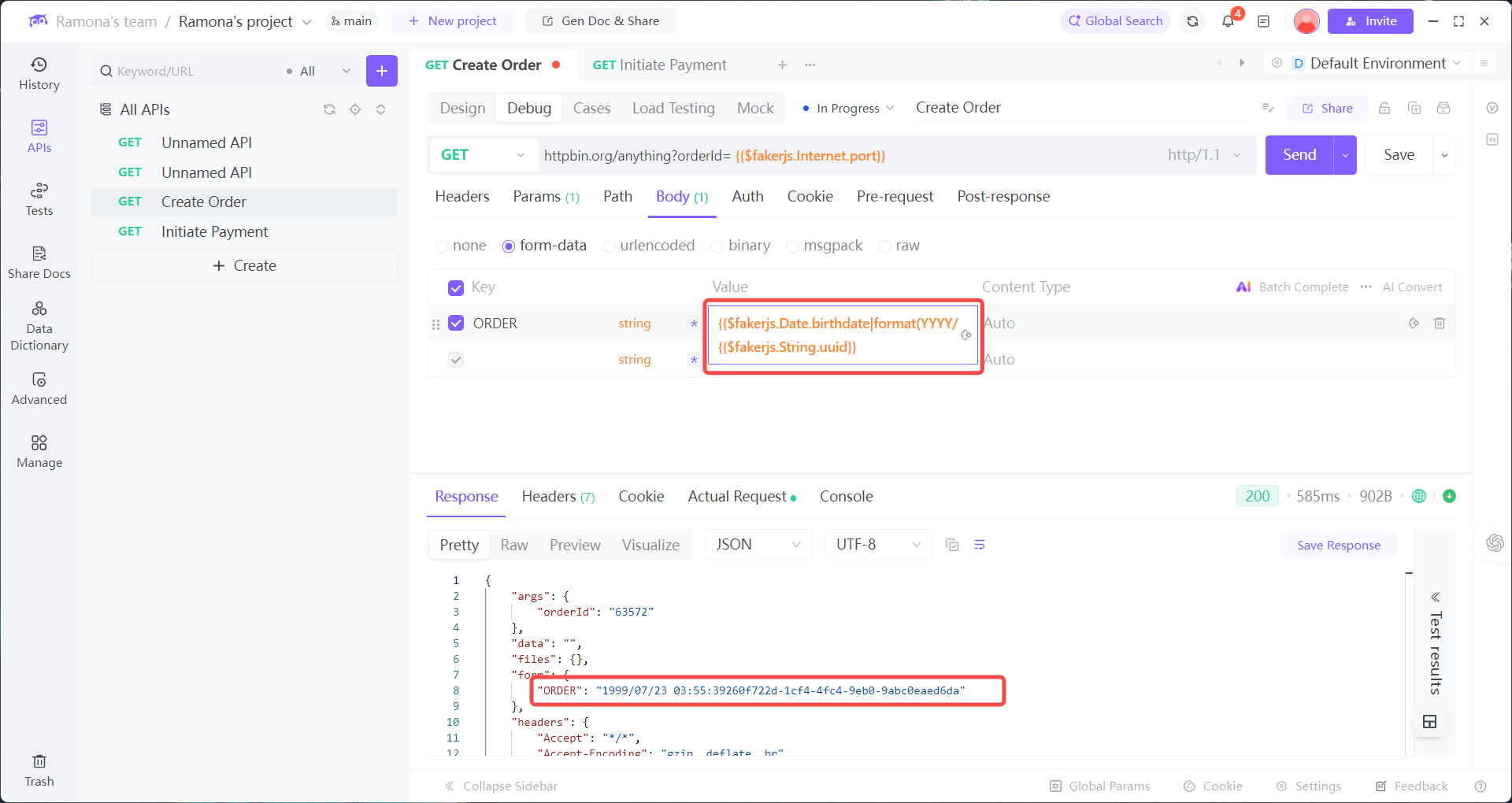
Built-in dynamic values cover the most common needs in API testing. They make handling time-related parameters, random test data, and environment identifiers effortless — cutting manual input and reducing errors, while boosting efficiency.
Custom Functions: Solving the Pain Point of “Custom Logic”
Custom functions allow developers to write scripts (e.g., parameter encryption, special formatting, custom validation) tailored to their business rules.
They address cases where built-in features aren’t enough. Common scripting languages like JavaScript are supported.
Example: Fintech API Parameter Encryption (Custom Logic)
A fintech developer is debugging a “Bind Card API” where the requirements are:
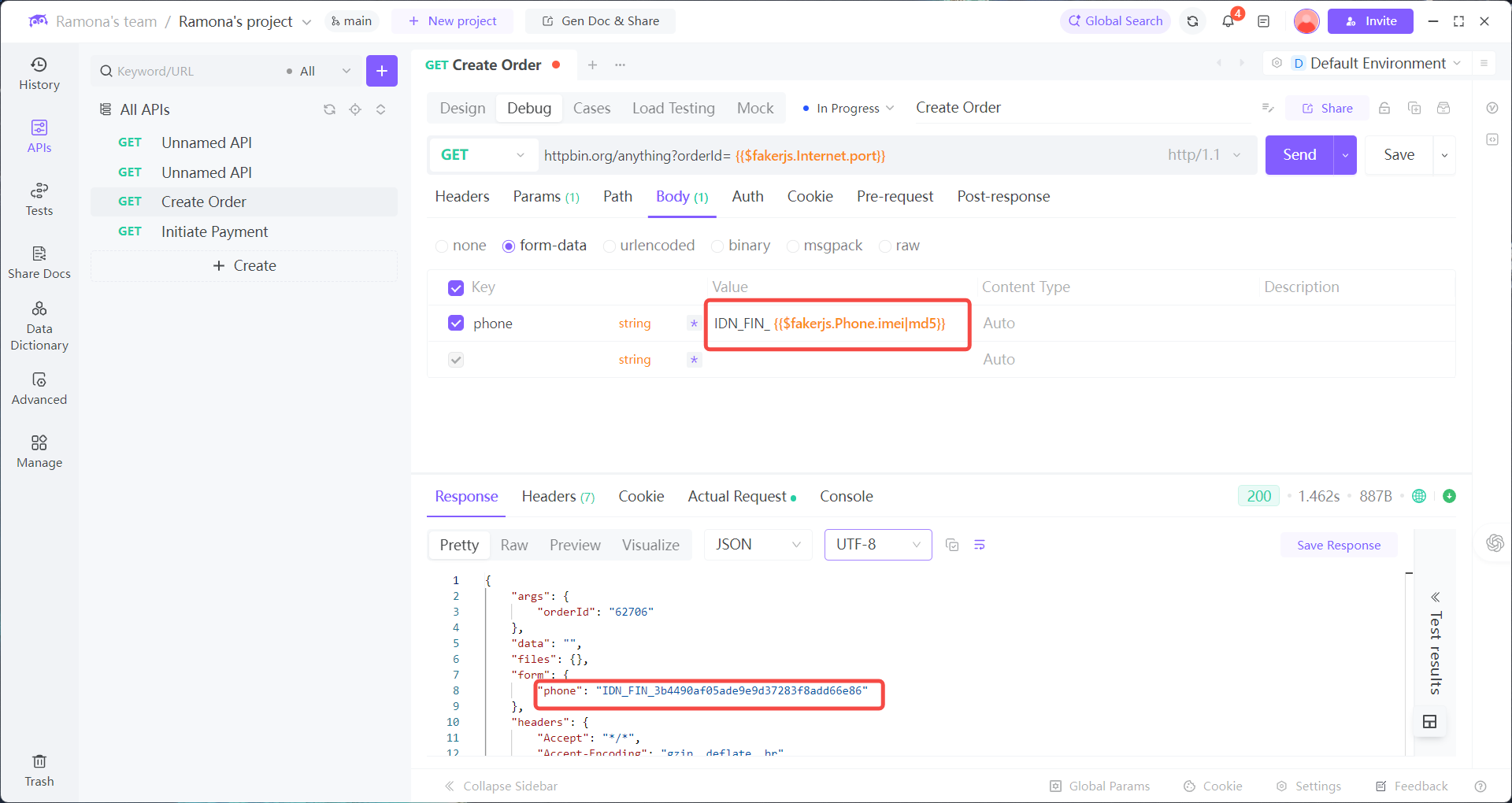
1. Sensitive parameters (e.g., phone number phone) must be encrypted with MD5 (custom platform rule, not a generic standard).
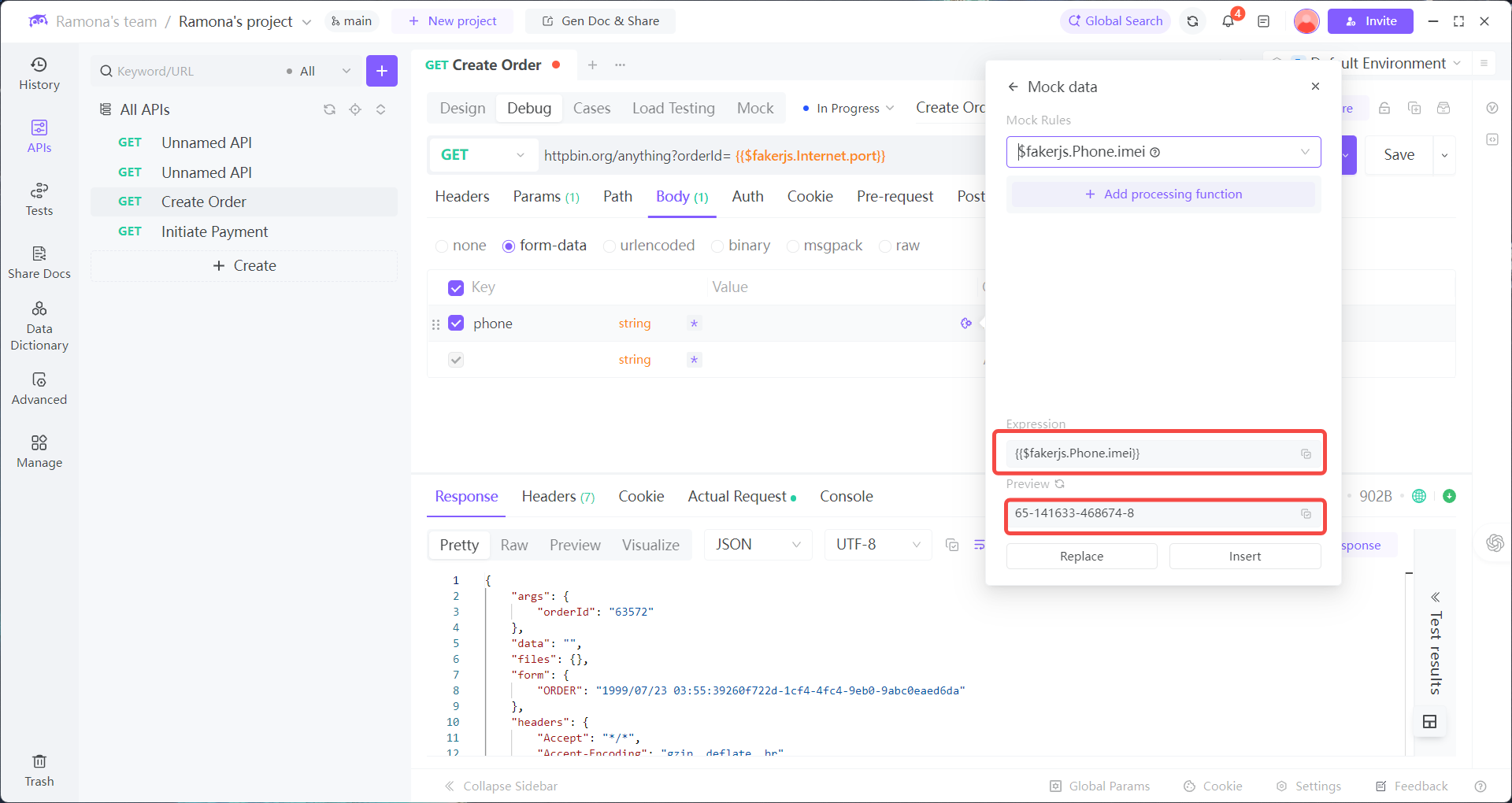
2. The encrypted value must then be prefixed with IDN_FIN_ (a business identifier) before being sent as a request parameter.
How to Apply a Custom Function
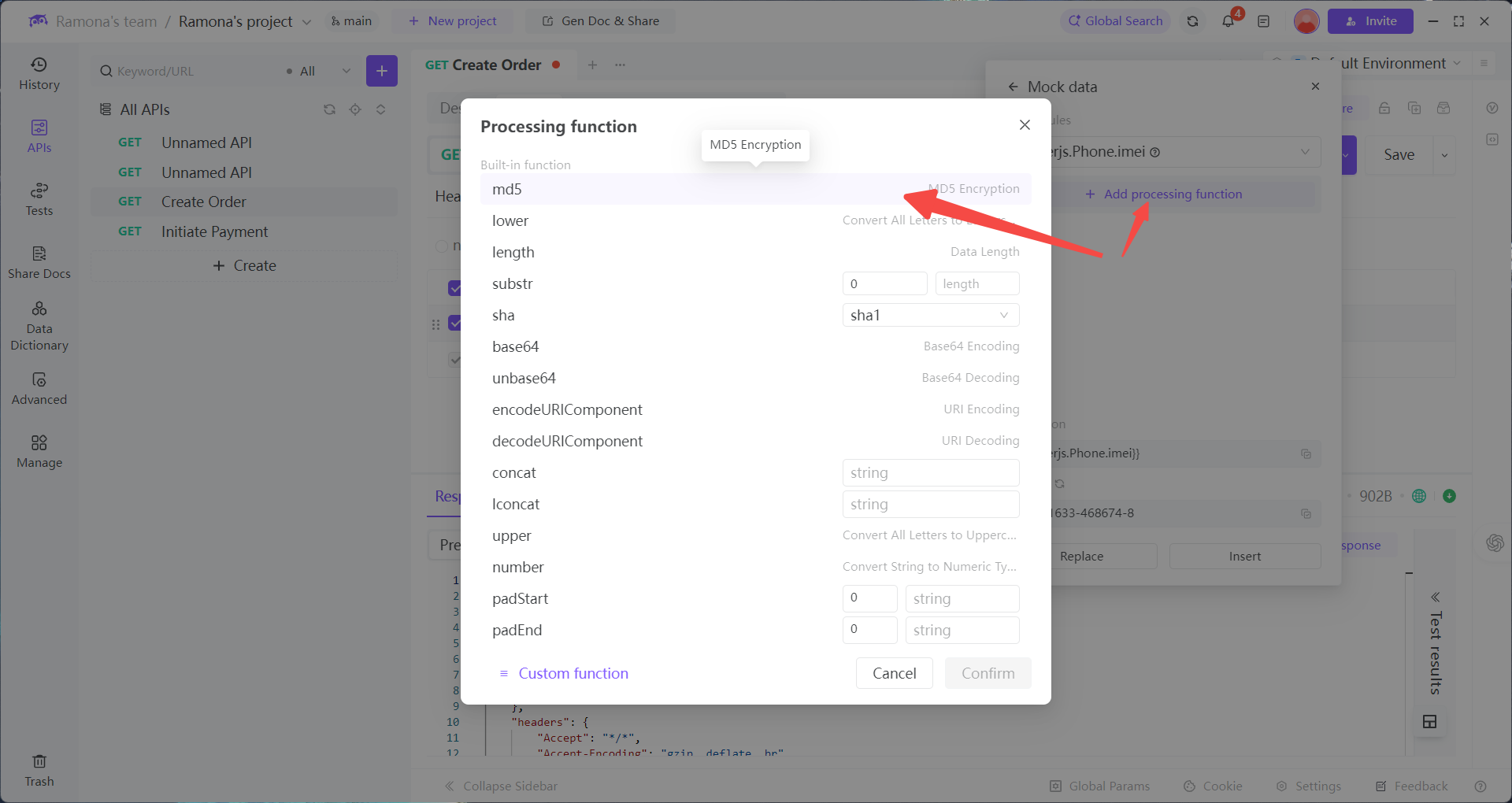
1. In EchoAPI’s Custom Function module, write an encryption script:
try {
// JavaScript does not have native MD5 support.
// This is a simplified mock (real MD5 is more complex).
let hash = 0;
if (text.length === 0) return hash.toString(16);
for (let i = 0; i < text.length; i++) {
let char = text.charCodeAt(i);
hash = ((hash << 5) - hash) + char;
hash = hash & hash; // Convert to 32-bit integer
}
return hash.toString(16);
} catch (e) {
return text;
}
Reference the custom function in parameter values
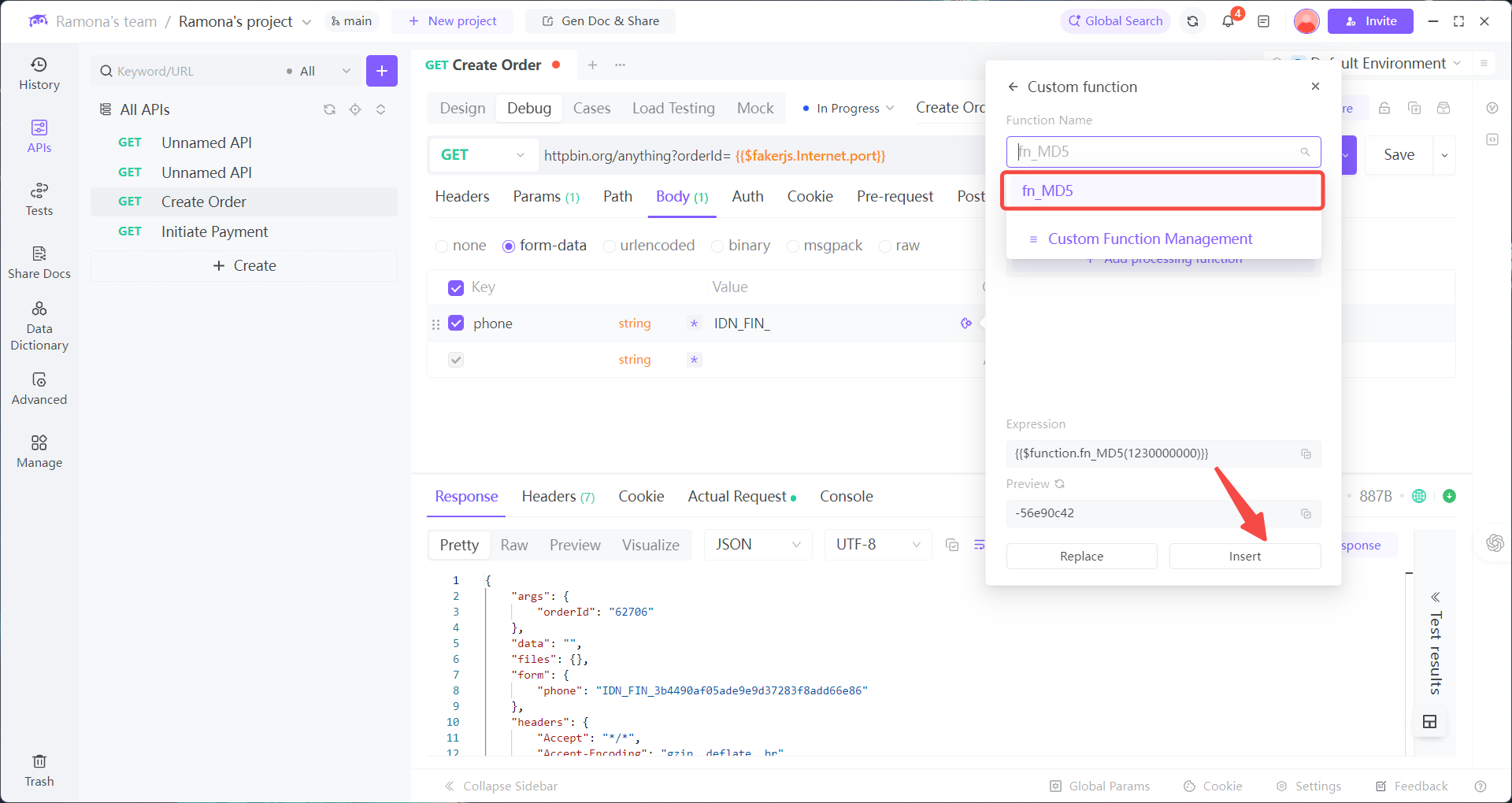
Enter your script and test the result
Click Create
Select Custom Function Management
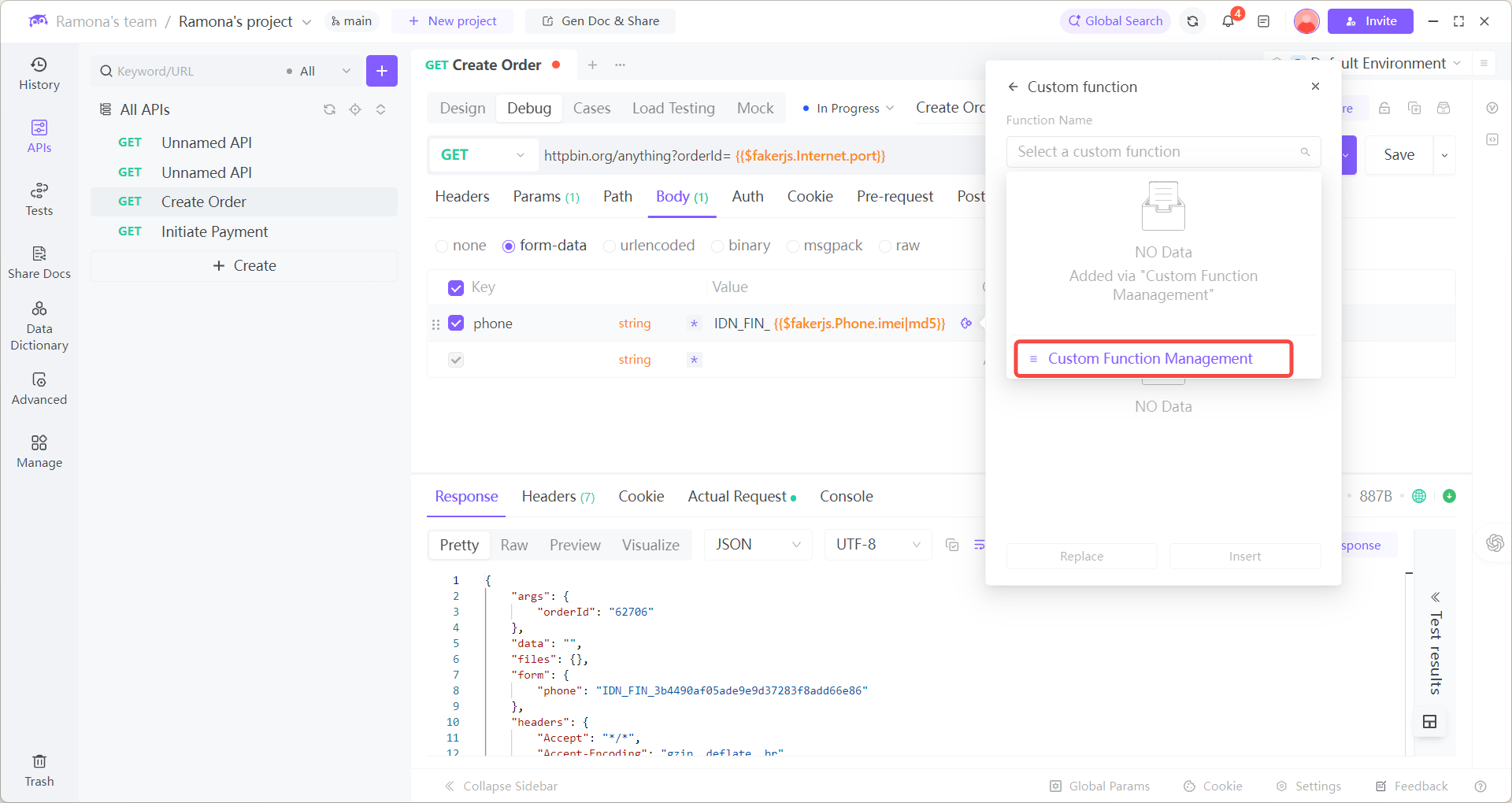
Click Functions
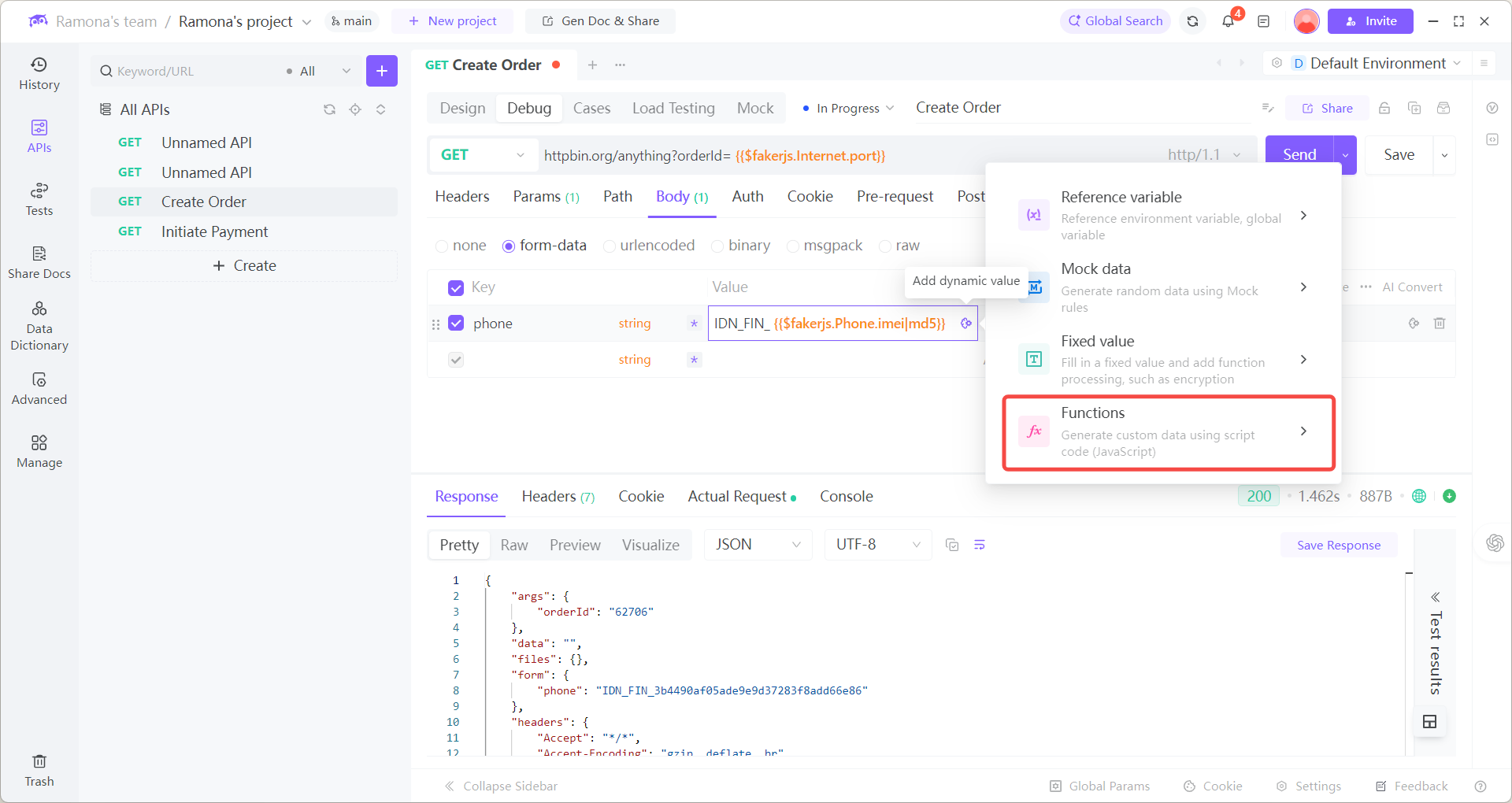
2. When calling the Bind Card API, in the phone parameter select:
→ Custom Function → MD5Encrypt
→ Enter raw value → EchoAPI will auto-encrypt and add the prefix.
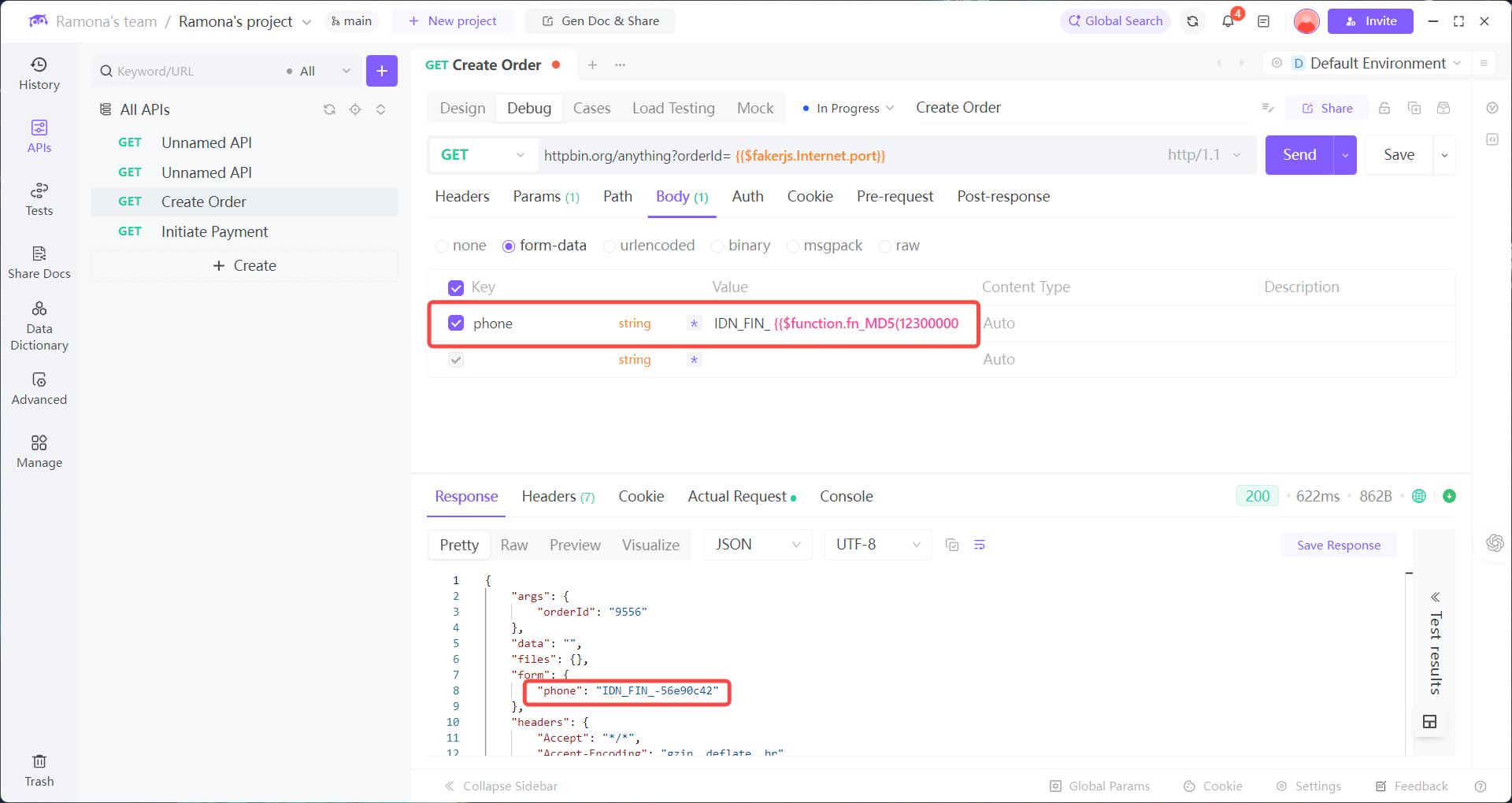
Key Advantages
- Custom business rules: Handle unique encryption rules (prefixes, non-standard algorithms) without external tools.
- Lower technical overhead: No need to set up a local crypto environment — write, debug, and reuse scripts directly inside EchoAPI.
- Compliance across regions: Easily adapt to region-specific requirements (e.g., Indonesia fintech prefix, US payment validation) without switching tools.
Built-in Custom Functions in EchoAPI
EchoAPI also provides a set of built-in functions, ready to use without writing code.
They cover common needs like string handling, data conversion, and encoding/decoding.
Combined with dynamic values, they dramatically speed up parameter handling.
1. String Functions
String functions handle text transformation and formatting — ensuring parameters meet API requirements.
| Function | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
strToUpper |
strToUpper(str) |
Convert to uppercase | strToUpper("hello") → "HELLO" |
strToLower |
strToLower(str) |
Convert to lowercase | strToLower("HELLO") → "hello" |
strTrim |
strTrim(str) |
Trim whitespace | strTrim(" test ") → "test" |
strPadLeft |
strPadLeft(str, length, padStr) |
Left pad with chars | strPadLeft("123", 5, "0") → "00123" |
strPadRight |
strPadRight(str, length, padStr) |
Right pad with chars | strPadRight("123", 5, "0") → "12300" |
strReplace |
strReplace(str, search, replace) |
Replace substring | strReplace("hello", "l", "x") → "hexxo" |
strSubstring |
strSubstring(str, start, length) |
Extract substring | strSubstring("hello", 1, 3) → "ell" |
strConcat |
strConcat(...strs) |
Concatenate strings | strConcat("a", "b", "c") → "abc" |
strLength |
strLength(str) |
Get string length | strLength("hello") → 5 |
strEncodeURI |
strEncodeURI(str) |
URI encode | strEncodeURI("a b") → "a%20b" |
strDecodeURI |
strDecodeURI(str) |
URI decode | strDecodeURI("a%20b") → "a b" |
Example Use Case: Normalize product IDs for a US e-commerce site by converting to uppercase and padding zeros.
2. Data Conversion Functions
These handle type conversions and data standardization.
| Function | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
toNumber |
toNumber(value) |
Convert to number | toNumber("123") → 123 |
toString |
toString(value) |
Convert to string | toString(123) → "123" |
toBoolean |
toBoolean(value) |
Convert to boolean | toBoolean("true") → true |
parseJson |
parseJson(str) |
Parse JSON string | parseJson('{"a":1}') → {a:1} |
stringifyJson |
stringifyJson(obj) |
JSON → string | stringifyJson({a:1}) → '{"a":1}' |
formatDate |
formatDate(timestamp, format) |
Format date | formatDate(1620000000000, "YYYY-MM-DD") → "2021-05-03" |
parseDate |
parseDate(dateStr, format) |
Parse date → timestamp | parseDate("2021-05-03", "YYYY-MM-DD") → 1620000000000 |
arrayJoin |
arrayJoin(arr, separator) |
Array → string | arrayJoin([1,2,3], ",") → "1,2,3" |
arraySplit |
arraySplit(str, separator) |
String → array | arraySplit("1,2,3", ",") → [1,2,3] |
Regional Adaptation: formatDate supports different locale formats, e.g.:
- Japan →
"YYYY年MM月DD日" - Indonesia →
"DD/MM/YYYY"
3. Encryption & Encoding Functions
Provide common encryption algorithms and encoding methods to meet API security requirements.
| Function Name | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
md5 |
md5(str) |
Compute MD5 hash | md5("hello") → "5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592" |
sha1 |
sha1(str) |
Compute SHA1 hash | sha1("hello") → "aaf4c61ddcc5e8a2dabede0f3b482cd9aea9434d" |
sha256 |
sha256(str) |
Compute SHA256 hash | sha256("hello") → corresponding hash |
base64Encode |
base64Encode(str) |
Base64 encode | base64Encode("hello") → "aGVsbG8=" |
base64Decode |
base64Decode(str) |
Base64 decode | base64Decode("aGVsbG8=") → "hello" |
hmacMd5 |
hmacMd5(str, key) |
HMAC-MD5 encryption | hmacMd5("hello", "key") → encrypted result |
hmacSha256 |
hmacSha256(str, key) |
HMAC-SHA256 encryption | hmacSha256("hello", "key") → encrypted result |
urlSafeBase64Encode |
urlSafeBase64Encode(str) |
URL-safe Base64 encoding | Replace + with -, / with _ |
Typical Use Case: Apply HMAC-SHA256 encryption to request parameters of an Indonesian finance API to ensure secure transmission.
4. Math & Logic Functions
Provide mathematical operations and logical conditions to support dynamic parameter calculations.
| Function Name | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
mathAdd |
mathAdd(a, b) |
Addition | mathAdd(2, 3) → 5 |
mathSubtract |
mathSubtract(a, b) |
Subtraction | mathSubtract(5, 2) → 3 |
mathMultiply |
mathMultiply(a, b) |
Multiplication | mathMultiply(2, 3) → 6 |
mathDivide |
mathDivide(a, b) |
Division | mathDivide(6, 2) → 3 |
mathRound |
mathRound(num, precision) |
Round to precision | mathRound(3.1415, 2) → 3.14 |
mathRandom |
mathRandom(min, max) |
Generate random number | mathRandom(1, 10) → 5 (example) |
ifElse |
ifElse(condition, trueVal, falseVal) |
Conditional expression | ifElse(1>2, "yes", "no") → "no" |
isEmpty |
isEmpty(value) |
Check if empty | isEmpty("") → true |
isEqual |
isEqual(a, b) |
Strict equality check | isEqual(2, "2") → false |
Typical Use Case: Calculate sales tax for US e-commerce orders (amount × taxRate), then round to two decimals.
5. System Utility Functions
Provide utilities related to the system environment.
| Function Name | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
getEnv |
getEnv(name) |
Get environment variable | getEnv("apiUrl") → returns env var apiUrl |
setEnv |
setEnv(name, value) |
Set environment variable | setEnv("token", "xxx") → sets token |
sleep |
sleep(ms) |
Delay execution (ms) | sleep(1000) → 1s delay |
log |
log(message) |
Print log to console | log("Request started") → logs message |
uuid |
uuid() |
Generate UUID | uuid() → random UUID |
timestamp |
timestamp(ms?) |
Get current timestamp | timestamp() → current timestamp (ms) |
Practical Use Case: Set environment variables before an API request, or insert debug logs in complex flows.
6. Key Features of Built-in System Functions
- Zero Configuration: All system functions are pre-built, ready to use without extra setup.
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Behave the same across EchoAPI main program and plugins.
- Composable: Functions can be nested to form complex logic.
// Example: Generate a signature with timestamp
try {
const timestamp = new Date().getTime();
const signature = `${text}-${timestamp}`;
return signature;
} catch (error) {
return text;
}
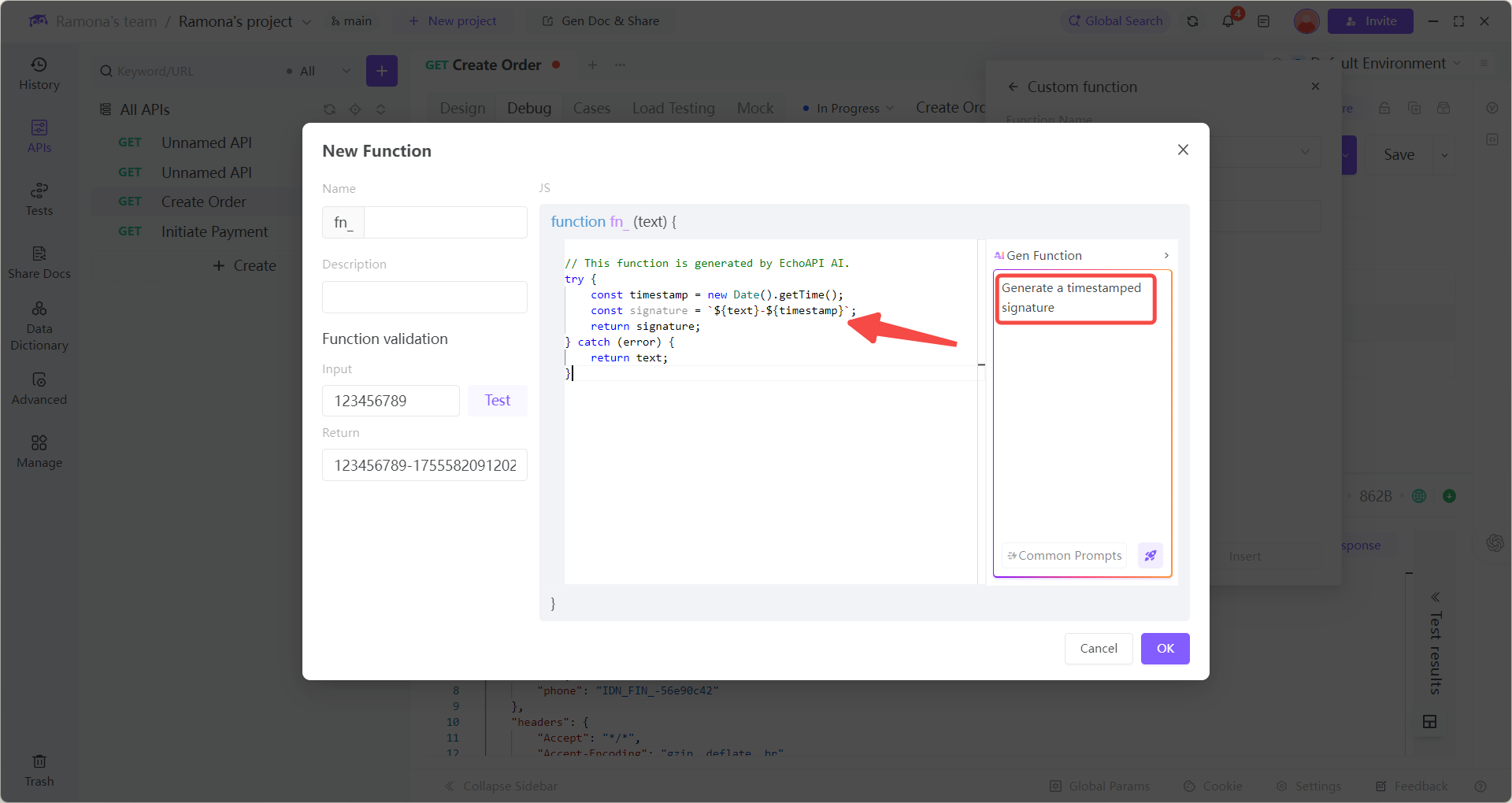
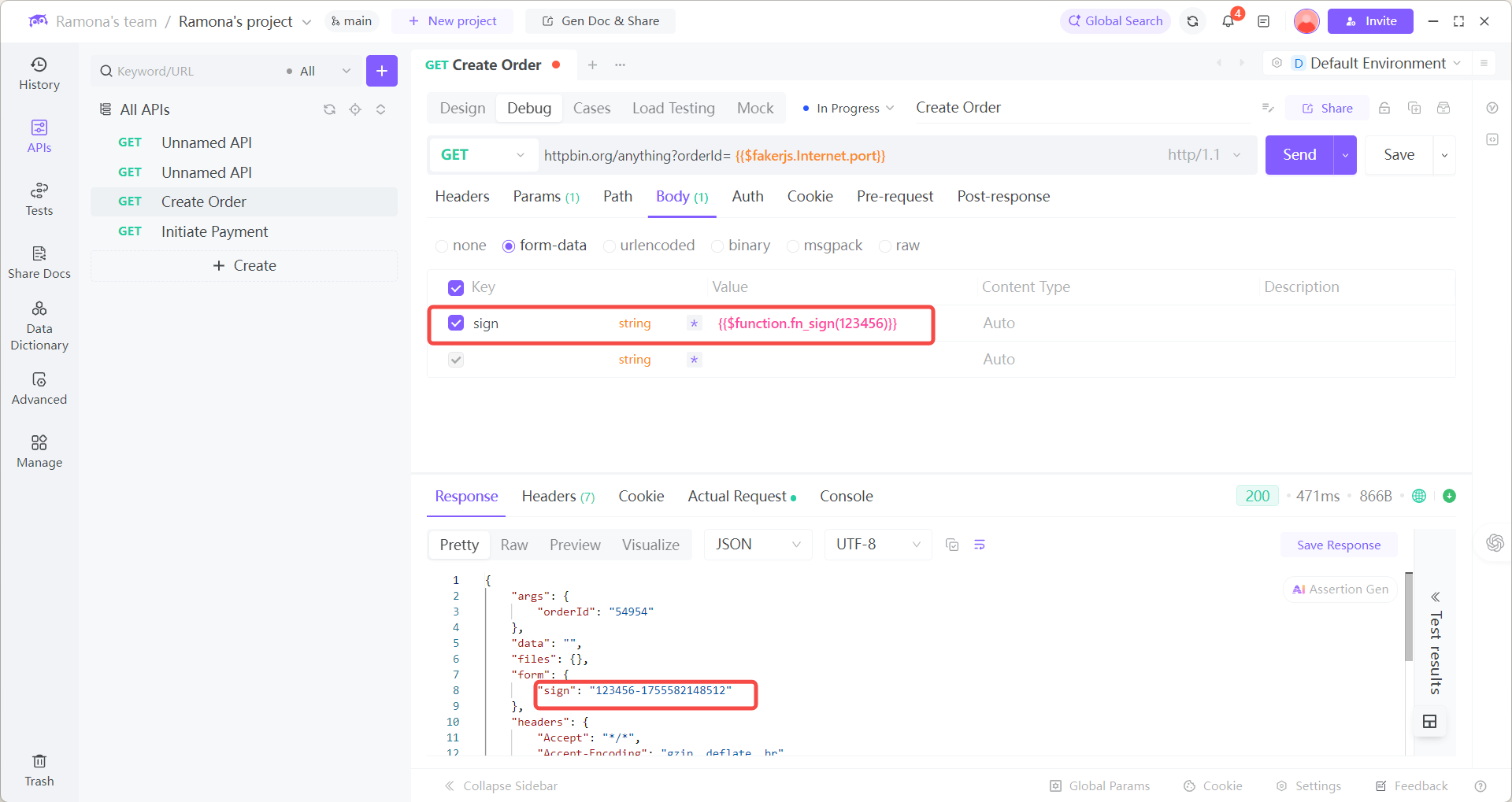
4.Offline Available: All functions execute locally without internet.
5.Regional Adaptation: Some functions (e.g., date handling) are optimized for regional formats.
System functions cover 80% of common API debugging needs. Together with dynamic values, they eliminate most manual scripting, making them ideal for fast testing and standardized parameter handling.
Summary: Core Value of Dynamic Values & Custom Functions
| Feature | Core Problem Solved | Extra Value for Multi-Region Developers |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Values | Handle dynamic parameters, cross-API dependencies | Auto-adapt timezones & formats, lower localization cost |
| Custom Functions | Handle custom logic (encryption, formatting, etc.) | Quickly adapt to business rules & compliance in different regions |
Together, they let developers focus on business validation rather than parameter handling, reducing repetitive work and minimizing human error. By leveraging dynamic values and custom functions, teams can quickly adapt to different API structures, localization requirements, and compliance rules, ensuring smoother integration across multiple regions.




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server








